Which State Had The Most Deaths From Heart Disease In 2021?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. The term heart disease refers to many different conditions that negatively affect the heart (via Mayo Clinic). Two of the most common types of heart disease are atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis is a condition in which plaque builds up on the walls of the arteries, narrowing them and making it difficult for blood to flow through. This can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become blocked or narrowed, again making it difficult for blood to flow through. This can also lead to a heart attack.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a major risk factor for heart disease. It occurs when the force of the blood against the artery walls is too high. This puts extra strain on the heart and can damage the arteries. Diabetes, which occurs when there is too much sugar in the blood, is another major risk factor for heart disease. Other risk factors for heart disease include smoking, high cholesterol, obesity, and a family history of the disease.
How Americans are affected by heart disease
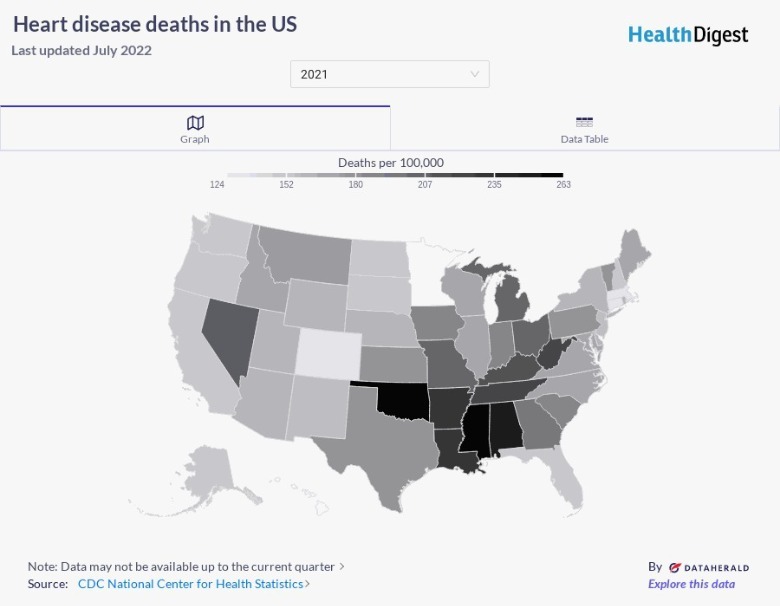
It's clear that heart disease affects a large number of Americans every year. However, there are still some stark differences between the percentages of people in each state who die from heart disease. For example, 252.9 in every 100,000 people living in the state of Oklahoma died from the disease in 2021, making it the state with the highest percentage of deaths that year. On the contrary, the state with the lowest percentage of deaths in 2021 was Minnesota, which recorded 115.1 deaths per 100,000 people. This means that Oklahoma experienced more than twice as many deaths per 100,000 people from heart disease as Minnesota.
Why do these numbers vary so much? According to CNBC, heart disease death rates are higher, on average, in red states than in blue states. There are a variety of factors that may contribute to this problem, including aging populations, smoking rates, poverty, and the availability of affordable healthcare. Racial disparities in healthcare also play a role, according to the University of Alabama at Birmingham. While many factors can affect someone's likelihood of developing heart disease, affordable healthcare is clearly a large part of the issue.