Powerful Medications That Can Be Dangerous To Stop Taking Suddenly
Taking your medications as prescribed is important, not only for managing your condition, but also to prevent other health problems from arising (via the Food and Drug Administration). Statistics pulled by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) around non-adherence to medication directions are concerning. Per the CDC, up to 30% of prescriptions remain unfilled, and approximately 50% of patients do not continue with their medication once prescribed. All told, approximately 125,000 deaths each year can be chalked up to people not taking their medication properly.
There can be numberous reasons why someone suddenly decides to stop taking their medication. These can include not being able to afford a refill, having unpleasant side effects, or deciding that the medication has already worked (and that taking it is no longer needed). However, neglecting to take your medication properly — or suddenly stopping it instead of tapering off gradually — can be a grave mistake. Doing so can lead to withdrawal symptoms, health problems and, in serious situations, even death. If you're taking any of the following medications, talk with your doctor first before deciding to stop taking them.
Blood pressure medications
For people with hypertension, managing it with medication can be a great way to keep it under control. Depending on what you have been prescribed, your blood pressure medication may control the speed of your heart pumping, lower the pressure in your blood vessels, or increase the amount of salt and water that is purged from your body. Given the critical roles that these medications play, it's important to take them as prescribed and to not suddenly cease taking them without first discussing it with your doctor.
If you decide to suddenly stop taking your medication, you could be exposing yourself to a wide array of health issues. These include damage to your arteries, an increased risk of stroke, renal problems or kidney failure, or damage to your optic nerve. When it comes to blood pressure medications, which tend to be taken daily, it's important to be prepared so that you do not run out. You could also ask your doctor about a 90-day supply, which will mean you will have to refill it less.
Antidepressants
Many times, according to Healthline, people who take antidepressants begin to feel better as a result of the medication working. They then assume that the antidepressants are no longer needed and stop taking them. However, this can be a serious misstep. Because many of the disorders that antidepressants treat involve rebalancing chemicals in the brain, stopping them suddenly can throw that balance off. And, due to the fact that most antidepressants can take four weeks or longer for their effects, it can take weeks to balance those chemicals again.
If you suddenly stop your antidepressant medication, you may experience withdrawal symptoms, including flu-like symptoms, dizziness, and stomach cramps, as noted by Medical News Today. In addition, your depression symptoms may return, leading to excessive crying, panic attacks, changes in mood, and suicidal ideation. You may also experience shock-like sensations, known as "brain zaps."
Ideally, you should only go off your antidepressant medication as advised by your doctor. And when you do, be sure to taper your doses, gradually lowering them until you are successfully off the medication.
If you or someone you know needs help with mental health, please contact the Crisis Text Line by texting HOME to 741741, call the National Alliance on Mental Illness helpline at 1-800-950-NAMI (6264), or visit the National Institute of Mental Health website.
Blood thinners
For people who suffer from such conditions as atrial fibrillation or deep vein thrombosis, blood-thinning medications such as apixaban (Eliquis) or rivaroxaban (Xarelto) can be helpful in preventing clots from forming. Stopping this drug (and those like it) early can increase your risk of blood clots forming, which could lead to a stroke or heart attack. If you need to stop taking Eliquis, then you should talk to your doctor about gradually tapering off the medication instead of going cold turkey.
If you use a drug such as Xarelto for an extended period of time, your body can get used to the way the medication interacts with your system. When you stop taking it suddenly, it can lead to withdrawal. Symptoms can include dizziness, fatigue, emotional disturbances, and nerve damage. The risk of stroke also comes with a compromised flow of oxygen to the brain, which can lead to a host of health problems, including partial paralysis and, in some cases, death.
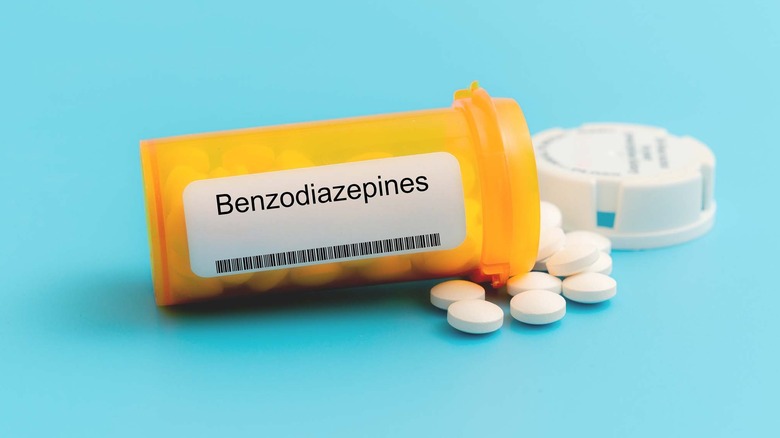
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines serve a number of purposes, including helping people recover from addiction and quelling anxiety disorders. They are also effective at dealing with symptoms of OCD and even calming people's nerves before surgeries or dental work. The downside is that people can build up a tolerance to them quickly, which can lead to a dependence. It can also mean that going off benzodiazepenes abruptly can throw your body into chaos.
According to the Benzodiazepene Information Coalition, going cold turkey on these medications can bring about withdrawal symptoms, including seizures, hallucinations, psychosis and, in some cases, even death. These withdrawal symptoms can take a serious toll on the body, causing damage to the central nervous system — damage that can sometimes take more than a year to heal from. In some situations, these withdrawal symptoms can become protracted, and it may take years of recovery before they are fully gone.
Gabapentin
There are a number of ailments that gabapentin can be prescribed to treat, according to Healthline. These include epileptic seizures, nerve pain stemming from shingles, restless leg syndrome, and neuralgia. For all its benefits, however, gabapentin can be very dangerous if you suddenly stop taking it. Even as you taper off the drug, you can experience such symptoms as fever, nausea, fatigue, dizziness, and headaches. But, if you stop taking gabapentin all at once, you run the risk of suffering from confusion, an irregular heart rate, or seizures so severe that they appear to almost be constant.
These symptoms can vary from person to person, with some people's symptoms subsiding within 12 hours and others taking up to seven days. There are several factors that can contribute to a person's dependency and subsequent withdrawal from gabapentin. How long a person has been taking it and how dependent they have become can all play a role in what a person goes through when deciding to stop taking it. A person looking to wean themselves off of gabapentin should only do so under a doctor's careful monitoring.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory drugs that have a wide range of applications, from treating asthma to managing the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. As noted by Medical News Today, they are a synthetic version of cortisol, a hormone produced by the body's adrenal glands. While you are taking corticosteroids such as prednisone, your body will produce less cortisol. As a result, when you suddenly stop taking the medication, your cortisol levels will drop and your body will not be able to immediately produce enough to balance those levels out. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including joint pain, low blood pressure, fatigue, and mood swings.
In addition, according to American Addition Centers, you can experience gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea. These withdrawal symptoms should abate within a week or so, but can be protracted in cases where corticosteroid use has gone on for a while. Medical News Today advises that if you experience these symptoms after stopping prednisone, you should consult your doctor.
Opioids
Opioids prevent pain signals from traveling through the body, and tend to be prescribed for the short term, due to the risk of dependency. It can be very easy to build up a tolerance to opioids, which can lead to the need to continually up the dosage in order to get the medication to work. There's also a risk of overdose, so caution has to be exercises when dealing with opioids.
Because of how powerful and addictive they can be, opioids present a great risk if one suddenly stops taking them. The Food and Drug Administration has noted the possibility of severe withdrawal symptoms stemming from abrupt cessation of opioid medication. These symptoms can run the gamut from anxiety to abdominal cramps, a loss of appetite, vomiting, and diarrhea. In addition, the body can experience severe, uncontrolled pain, and a person who stops taking opioids may also experience suicidal ideation. If you have been taking opioids for two weeks or longer, you should consult with your doctor about how to taper off slowly and safely.
Muscle relaxants
Muscle pain can impact day-to-day life, making it hard to move, enjoy physical activity, or even just to go about your day. Muscle relaxers such as Soma, Flexeril, and Zanaflex block pain signals to the brain, thereby giving your muscles some breathing room and allowing them to relax. Because muscle pain can impact daily life, the medication used to combat that pain can become addictive very quickly. People who need muscle relaxers just to function may find themselves taking them even when they no longer need them. However, stopping them suddenly can throw the body into crisis, causing such symptoms as tremors, hallucinations, seizures, and even psychosis.
The symptoms for people going through muscle relaxer detox can be prolonged, with the timeline for withdrawal hinging on how long the drug has been taken. In general, they can last for a few days, but can also go on for a few weeks in some cases. Working with your doctor can help you to stop taking muscle relaxers safely, while also making sure that you are still addressing your pain effectively.
Proton pump inhibitors
For people who suffer from gastric disorders, proton pump inhibitors can be a blessing. These medications work by decreasing the amount of acid produced by the stomach, and are effective against such conditions as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Some people who take these medications have become concerned about the potential side effects of proton pump inhibitors, including the risk of either kidney or heart disease. As such, they may be inclined to stop taking them immediately. However, that is not advisable.
Because of the way the proton pump inhibitors work to suppress stomach acid, immediately hitting the brakes on them can cause your stomach to overproduce acid in a condition known as rebound hyperacidity or acid rebound (via Tampa Bay Reflux Center). According to GoodRx Health, acid rebound can be as painful, if not worse, than GERD. It can impact people who have been taking proton pump inhibitors for as little as two months. Symptoms (which include nausea, burning in the throat, and a chronic cough) can appear as quickly as two weeks after stopping the medication.
By slowly lowering your medication, changing medicines, and altering your lifestyle to prevent conditions such as GERD, you can reduce your risk of experiencing rebound acidity.