When You Don't Use Sunscreen, This Is What Happens To Your Skin
Having a good tan is as fundamental to summer as pool parties and barbeques. And believe us when we say that the cosmetics industry knows this better than anyone else. In 2021, the global market size of self-tanning products reached almost $900 million, and it looks as though that's only due to grow as time goes on, as more and more people clamor for that perfect bronzed look (per Grand View Research).
But there's one thing, and one thing alone, that works better than anything else to give us a healthy glow. Getting the sun on our skin is second-to-none, but in the endless pursuit of an all-over tan, it might be tempting to skip the sunscreen. We can see why it might seem sensible to do so: After all, sunscreen is expensive (and with a healthy $520.4 million U.S. market valuation for 2022, per IBISWorld, the industry is by no means struggling), and just a bit fiddly to put on, and then there's the smell, and surely it's just blocking your tan, right? And what's the worst that can happen if you don't wear it? We're here to show you just that. Let's take a look at what happens to your skin when you don't use sunscreen.
How does sunscreen actually work?
Sunscreen is one of those things that we somewhat absentmindedly slather on our skin, and although we know that it's good for us, we're not really sure how this miracle lotion works. So let's clear this up.
Sunscreens protect our skin from sun damage through the inclusion of active ingredients that work to block two types of sun rays, UVA and UVB (per Good Housekeeping). UVA rays are the ones that make your skin age, and UVB rays are the ones that cause it to burn. When these active ingredients are combined, a good sunscreen will effectively safeguard your skin from the most damaging aspects of the sun.
Sunscreens are often classified by their Sun Protection Factor (or SPF) number. The SPF number is a multiple of the time that it would normally take you to burn (so, for example, if you had an SPF 30 sunscreen, it'd protect you for 30 times longer than if you weren't wearing anything). The specific ingredients that are used in sunscreen vary from product to product, with mineral sunscreens utilizing the sun-reflecting power of zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, and chemical sunscreens using active ingredients that absorb UV rays, like homosalate or avobenzone.
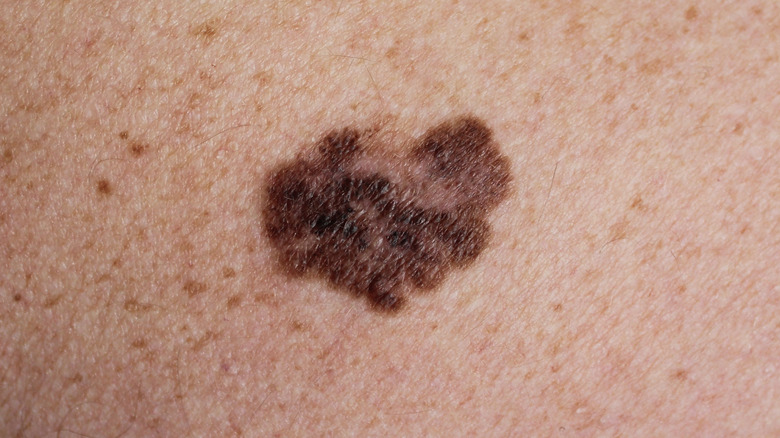
Not using sunscreen can lead to an increased likelihood of skin cancer
One of the most consequential aspects of omitting sunscreen from your skin care regimen is the increased risk of developing skin cancer due to repeated sun damage (via Skincare.com). In fact, that's the very reason sunscreen was invented — and researchers have found that it's not only UVB rays that can be damaging, but UVA rays as well. "We suspected for years that these rays caused sun damage in the form of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (two forms of skin cancer)," says Skincare.com expert and board-certified dermatologist Lisa Ginn. But as Ginn states, recent research proved that UVA ray damage may also be behind melanoma, a the most severe form of skin cancer (per WebMD).
To reduce the risk of developing melanoma, as well as other skin cancers, it's highly important to wear sunscreen — and not just in the summer. Applying products that are SPF 30 or higher year-round is the best way to ensure that your skin is well-protected. Don't be fooled by cloudy conditions, either, as you can still experience sun damage when it's overcast.
Without sunscreen, you might see more broken blood vessels
Let's face it: We all want our skin to be blemish-free. But if you skip the sunscreen, you might find that your skin starts to look a little less flawless, through the presence of broken blood vessels. "Broken capillaries on the face and around the nose can be caused by a variety of conditions. Most commonly, the cause is sun damage," says Obagi Skin Health Institute cosmetic dermatologist Sameer Bashey to InStyle. As the sun goes to work on our skin, reducing the thickness of our dermis layer, certain components of our skin like elastin and collagen get less voluminous. Our capillaries are then able to rise to the surface, with the damage to them becoming more visible.
The solution? You've got to wear your sunscreen, folks. A sunscreen with a high SPF number applied regularly will protect your skin and prevent your dermis from thinning. If you already have broken capillaries that you want to address, Bashey advises that laser treatments are available, although you may experience some bruising, pain, and tenderness after any cosmetic procedure to target them.
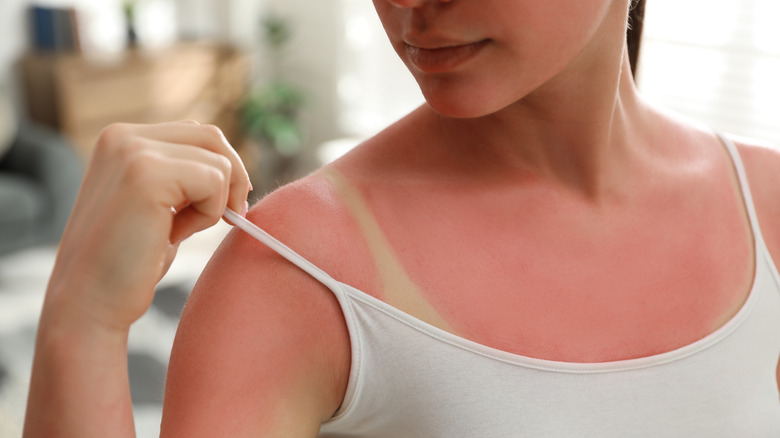
Your skin will burn without sunscreen
So, we're probably not going to win any prizes for subtlety with this one. But you know what? It bears mentioning: If you don't wear sunscreen, you're gonna burn. What's particularly interesting, though, is how this actually happens. "When we think of a burn, we think of heat. But it's not the sun's heat that burns our skin. Sunburns are from ultraviolet radiation — or UV rays — causing damage to the skin," explains Saira George, dermatologist for the MD Anderson Center.
When UV rays land on our skin (whether that's directly or through the clouds), it starts to impact it immediately, altering the skin's DNA. While your skin may be able to handle this for a short amount of time, eventually it reaches a tipping point, and these UV rays start to kill your skin cells. Our bodies then prompt an increase in blood flow to the surface of the skin to deliver immune cells in an attempt to heal the damage — and it's this that makes our skin red and painful. By using sunscreen, you prolong the amount of time it takes for the UV rays to impact your skin in the first place, keeping sunburn at bay.
Skip the sunscreen, and your skin will age faster
Our skin aging is a natural part of life: Sooner or later, you're going to get some wrinkles. But how you treat your skin is an important factor in the speed by which it ages visibly, and forgetting to put sunscreen on may have it looking older even quicker. While the effects of the sun on visible skin aging — and sunscreen's ability to prevent it — used to be merely assumed, a 2013 study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine conclusively proved these beliefs to be the case.
Researchers looked at what happened to participants when they wore sunscreen every day over four and a half years, and what happened when they didn't. And the ones who wore sunscreen? Their skin didn't appear to age in response to the sun and potential damage, and overall was 24% less likely to have shown signs of aging at all. We mean, it doesn't get much more persuasive than that on the wearing-sunscreen front, does it?
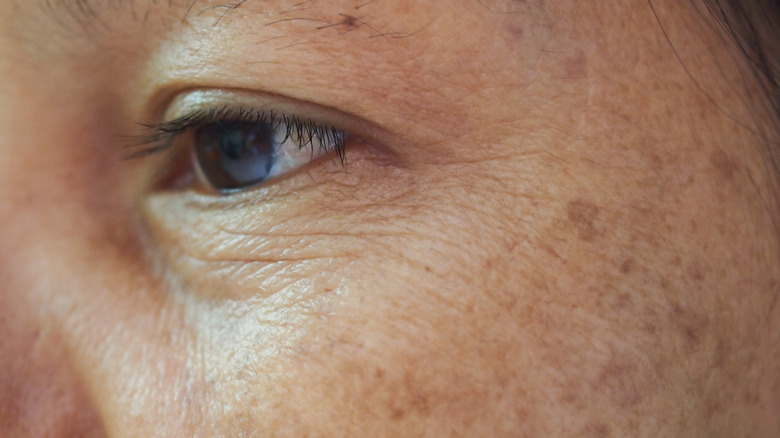
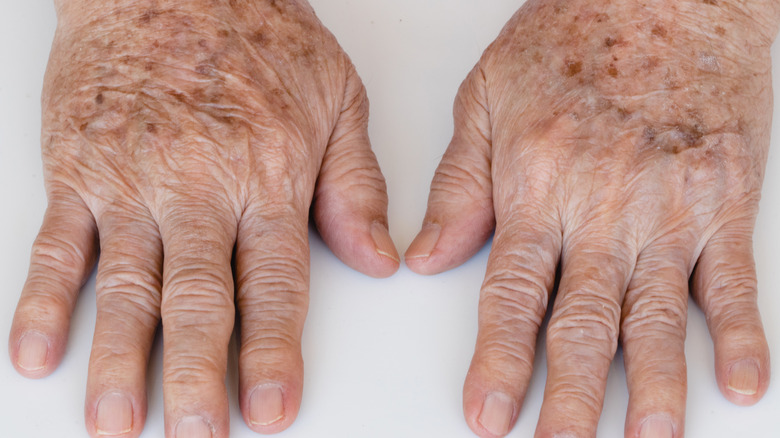
You'll likely see more age spots without using sunscreen
As we grow older, our skin changes with us (via MedlinePlus). Wrinkles, fine lines, and changes in skin texture are all part of the rich tapestry of moving through life. Age spots — dark marks on your skin that can look similar in appearance to freckles or moles — are also part and parcel of the aging process (per the Mayo Clinic). But as these spots are exacerbated by sun damage, if you're not wearing sunscreen, they can appear with more frequency and visibility.
Once you have age spots, they're unlikely to fade, making them distinct from freckles, which tend to wane if your skin doesn't come into contact with the sun. They'll generally be more common in the areas that have the most exposure to the sun: The backs of your hands, face, and shoulders are particularly common zones for age spots to appear. While age spots aren't dangerous, it's useful to keep an eye on them to see if they change over time. If your age spots appear to be getting bigger, turning black, or are irregularly shaped, it's advisable to have them checked by a doctor, as this could be a sign of damage and potentially melanoma, the Mayo Clinic says.
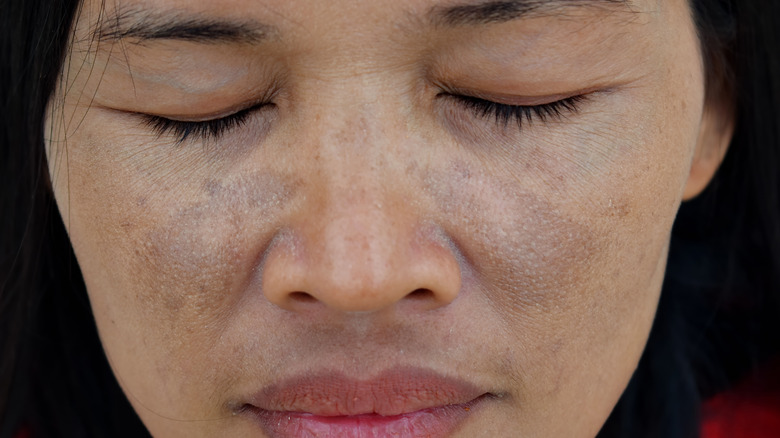
You might see some uneven discoloration on your skin
The sun can provide our skin with an often-desired tan, but if you skip the sunscreen too often, this color change can be uneven. For people with darker skin, increased exposure to the sun may result in a discoloration known as hyperpigmentation. "The darker your skin, the more reactive your melanocytes are. Sun exposure triggers melanocytes to turn on and produce more melanin," says the Skin of Color Society spokesperson, the University of Miami Department of Dermatology's Skin of Color Division director, and dermatologist Heather Woolery-Lloyd to Livestrong. When this happens, your skin may change tone unevenly, with discoloration, darker patches, and freckles all appearing.
Another potential result of sun exposure without sunscreen is melasma, which again may cause discoloration and blotches across the skin. Unfortunately, the consequences of this can extend far beyond the skin's appearance. "People with skin discoloration like melasma have a high incidence of low self-confidence, which interferes with their quality of life," explains UCLA's David Geffen School of Medicine's clinical professor of dermatology Tanya Kormeili to Livestrong. The best preventative measure for developing conditions like melasma or hyperpigmentation, aside from staying out of the sun, is to whip your sunscreen out.
In some cases, you might see some scarring if you don't wear sunscreen
When it comes to the sun, getting burned isn't the only risk you take if you spend too long in it. Failing to protect your skin with sunscreen may cause particularly notable consequences for people with chronic conditions. "In patients with underlying photosensitive disorders such as lupus, direct UV rays can exacerbate their disease and in some cases lead to scarring," says Schweiger Dermatology Group's Lotika Singh to Bustle. Other issues that can be caused by the sun for people with lupus include itching and skin rashes, alongside lupus symptoms like weakness, joint pain, and even potential damage to the organs (per Healthline).
Psoriasis, a long-term disease that affects the skin, is another condition that may be affected by a lack of sunscreen. Flare-ups of psoriasis can occur due to increased exposure to the sun, and putting sunscreen on your skin may keep it at bay, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation. If you have psoriasis, make sure to put sunscreen on your plaques as well as any other exposed areas.
You may tan faster without sunscreen -- but be careful
For naysayers of applying sunscreen, there's a common refrain given for their lack of lotion: "You can't tan through sunscreen!" And they may have a point. Applying sunscreen does reduce the speed by which you tan, according to Healthline. This is because sunscreen works to dispel or reflect the UV rays that activate your melanocytes, prompting the melanin in your skin to be produced (per Nemours TeensHealth).
However, just because sunscreen helps protect against these UV rays doesn't mean it entirely blocks them. Sunscreen is essentially a filter for ultraviolet radiation, which can still get through and permeate the skin — so you can still tan while wearing your spray or lotion (via Healthline). What's vital, though, is to remember that not wearing sunscreen with the express purpose of tanning is a risky business. Seemingly minor amounts of sun exposure can have a cumulative effect, and avoiding sunscreen in the pursuit of a tan leaves you not only at risk of some unpleasant burns, but also, more worryingly, an increased risk of long-term skin conditions.
You won't get more vitamin D if you don't use sunscreen
Getting adequate levels of vitamin D is paramount to keeping your health intact, with the nutrient helping to support everything from immune function to strong bones (per Medical News Today). And with one of the best sources of vitamin D coming from that great big ball of fire in the sky, it's understandable that some people might want to maximize their vitamin exposure by avoiding sunscreen. But it's important to remember that sunscreen and proper vitamin D levels are perfectly capable of co-existing.
"Studies have never found that everyday sunscreen use leads to vitamin D insufficiency. In fact, people who use sunscreen daily can maintain their vitamin D levels," says the Skin Cancer Foundation. We don't need that much sun for our bodies to produce the levels of vitamin D we require, and although sunscreen does indeed filter out the majority of UVB radiation, our skin still receives some of the rays. Bear in mind, too, that the sun isn't the only source of vitamin D out there. Dietary sources like fortified milk products, fatty fish, and eggs can deliver your daily dose, and if you're not getting enough from what you eat, taking supplements is a great way to top up.
Your skin may become more leathery without sunscreen
Smooth, supple skin: It's what most of us want. Or at least, most of us want our skin not to be tough (and we're not talking in the emotional sense). But unfortunately, if you're avoiding the sunscreen, your skin may pay the price and lose a lot of its pliability over time. This is according to research published in the Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, which looked at the effects of UVA radiation on the elasticity of the skin of mice. Researchers found that for mice who weren't treated with any sunscreen, their skin became less elastic, increased in thickness, and took longer to spring back into shape when pinched (poor mice!).
For mice that did have sunscreen applied, though, their skin retained much of its elasticity. It's important to bear in mind, of course, that this was a rodent study, and so there may be differences in the impact on human skin. But regardless, it looks like yet another reason to cover up.
What sunscreen should I be using?
So, you've decided that sunscreen is, in fact, a wise thing to use. Congratulations! We're with you on that one. But the next logical question is, which one do you choose? The sunscreen market is a whirlwind of abbreviations and uncommon ingredients, so picking the perfect one is understandably tricky. First off, make sure that your sunscreen is labeled as "broad-spectrum," which means that it'll protect from both UVA and UVB rays, the Skin Cancer Foundation states. This will give your skin the best protection possible.
Next it's time to consider your SPF. Opting at a minimum for SPF 30 is advisable according to New York-based dermatologist Adarsh Vijay Mudgil, who calls it the "magic number" (via Better by Today). SPF 30 gives you a strong protection factor, blocking 97% of the harmful UVB rays. Finally, think about your skin's individual needs. "If you have acne or oily skin, make sure that your sunscreen is labeled as 'non-comedogenic,' which means that it has been shown not to block pores," advises Mount Sinai Hospital dermatology department's director of cosmetic and clinical research Joshua Zeichner to Better by Today. Drier skin types might wish to choose a sunscreen with a built-in moisturizer.
What skin parts are particularly important to cover with sunscreen?
When it comes to sunscreen, you're going to want to make sure that you have good coverage of anywhere that's going to be exposed to the sun, applying it thoroughly before you go out (per the National Health Service). But there are some specific body parts that you're going to want to tend to. The eyelids are one spot that people tend to miss, with a pretty large percentage of people failing to cover their eyelids (or even realizing that it's important to do so) in a study published in PLOS One. Given the thinness of the skin in your eyelids, it's important to make sure they're tended to.
Also of concern is how people treat their lips. Your lips are particularly low on melanin, meaning that they have less protection from the sun than other body parts, says Everyday Health. It's useful to put on a lip balm that has an SPF of 15 or more to keep them from burning. And whatever you do, don't put on lip gloss. "The more hydrated your lips are, the easier it is for UV rays to penetrate deeper into unprotected skin," warns New York University Langone Medical Center's clinical associate professor of dermatology Doris Day to Everyday Health.