When Should You Be Concerned About Bruises?
We are all susceptible to the occasional bump, scrape, or bruise. Bruises are temporary injuries that result from trauma inflicted to the tissue below the skin (via State Urgent Care). In some instances, small amounts of blood can leak out from the surrounding veins or capillaries if they've been damaged. What you observe as a bruise on the skin's surface is discoloration from the red blood cells that have collected underneath.
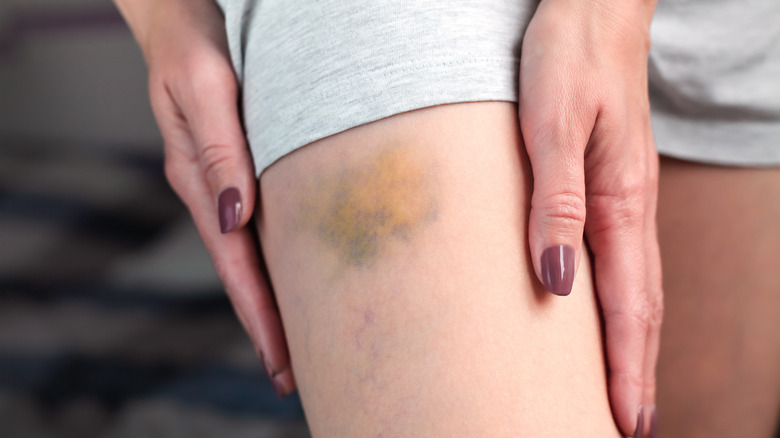
From the time a bruise emerges to when it heals, it goes through different phases and changes in color. A fresh bruise usually starts out red in color (per Medical News Today). After a day or two, the bruise may appear black, blue, or purple as the red blood cells underneath the skin progressively lose oxygen. Within five to ten days, your bruise will likely appear a shade of green or yellow as the body releases compounds to break down the hemoglobin in the blood. By day 14, your bruise should be on the mend and may appear yellow-brown or light brown in color as it continues to fade.
Typically, bruises will resolve on their own within two weeks. However, there are instances in which a bruise may warrant medical attention.
A bruise may be cause for concern if accompanied by other symptoms
Some people — including women and those over the age of 50 — may be more prone to bruising than others, according to Mayo Clinic. People who are on blood thinners or take certain supplements also may bruise more easily. Plus, those diagnosed with hemophilia — a blood clotting disorder that affects 400,000 people across the globe (via Hemophilia Federation of America) — are at an increased risk for bruising.
If you experience bruising along with additional symptoms, it may be time to see a doctor. Swelling around the bruised skin, a lump under the skin, or loss of function of a joint, muscle, or limb in the affected area should be professionally examined (per State Urgent Care). Also, consult your doctor if you experience impaired vision, abnormal bleeding in the gums, frequent nose bleeds or blood in the urine or stool, or if a bruise appears underneath a nail (via WebMD). Any bruise that does not improve within two weeks also should be examined by a physician.
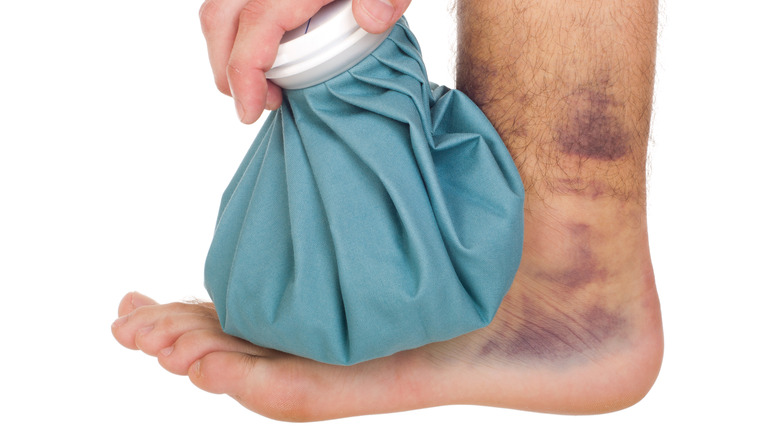
You can help speed up healing with some at-home care. According to State Urgent Care, a cold compress can help reduce inflammation. Additionally, both compression and elevation can offer healing benefits. Compressing the area with a soft elastic wrap during the daytime within the first 24 to 48 hours following the trauma can help reduce discomfort, while elevating the bruised area above the heart can slow bleeding.