Can You Put Sunscreen On A Sunburn?
Spending the day at the beach might sound exciting, but it's also important to consider how our skin will respond to it. Our skin is the largest organ in our body and is made up of three layers — the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis (via WebMD).
The hypodermis is the skin's innermost layer and is composed of fat and tissues. The dermis is the middle layer found between the hypodermis and the epidermis and contains hair follicles, sweat glands, and connective tissues. The epidermis is the skin's outermost layer that serves as a protective barrier and determines skin tone. Of all the elements our epidermis protects us from, experts at WebMD emphasize how it also plays a crucial role in protecting us from UV light and other harmful sunrays. The epidermis also contains melanin-producing cells, so when our body is exposed to the sun for long periods of time, this results in tanning — the body's natural way of avoiding sunburns (via Verywell Health).
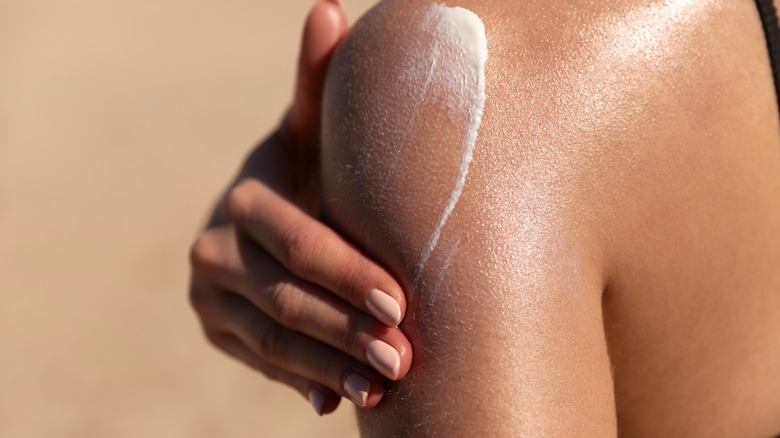
We can further protect our skin from sunburns by using moisturizers and sunscreens, but are these effective after the skin is already sunburned? Can sunscreen actually provide relief against sunburns? Let's find out!
Here's how sunscreens respond to sunburns
Untreated sunburns can lead to serious health problems like skin cancer. This is where sunscreens come in handy by deflecting, scattering, and absorbing sunlight. Sunscreens can be classified into two types — physical and chemical sunscreens.
Physical sunscreens are layered on top of the skin and work by reflecting the sun's rays. Chemical sunscreens, on the other hand, absorb UV rays into the skin and release them outwards in the form of heat (via Piedmont Healthcare).
Sunscreens can prevent sunburns, but are they equally as effective after you get a sunburn? Dr. Debra Jaliman, a dermatologist, weighs in and suggests that sunscreens containing zinc oxide may help with the swelling, as it is an anti-inflammatory compound (via Fashionista). Similarly, moisturizing aids the body's natural healing process.
While sunscreens may help with sunburns to an extent, you should be careful of other chemicals — such as trolamine salicylate — used in sunscreens as they may irritate the burn (via The Healthy). Instead, the FDA recommends using sunscreens containing zinc oxide, oxybenzone, and aminobenzoic acid (via FDA).
Alternative ways to treat sunburns
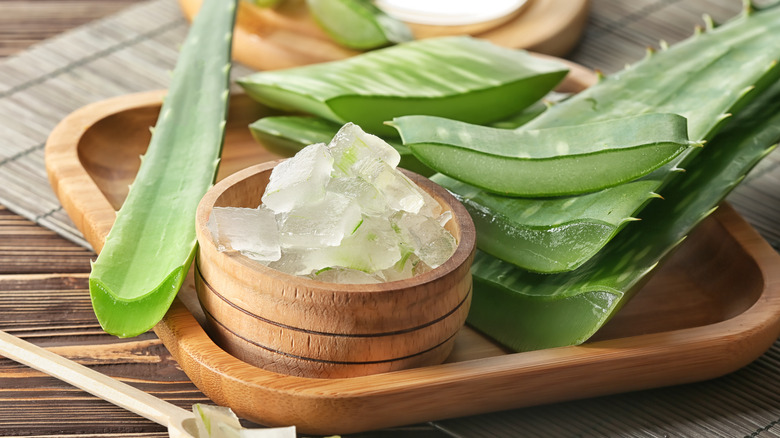
Sunscreens aside, there are other easily available means that can help you treat a sunburn — some of which can be found in your own kitchen! Some other popular methods for treating a sunburn include using aloe vera gel or moisturizer, taking cool baths, avoiding heat or direct sun, hydrating plenty, and wearing breathable clothes (via American Academy of Dermatology Association).
If you have blisters from a second-degree sunburn, avoid using sunscreen to treat it. Instead, cover the affected area with protective clothing and do not pop the blisters as it may lead to an infection (via Healthline).
Sunburns can be nasty, so prevention is the best form of defense. The most convenient and effective way to avoid a sunburn is to apply sunscreen. It is recommended that you apply sunscreen every 2 hours while outside, especially after swimming, sweating, or drying off (via FDA).