Hypothyroidism Vs. Hyperthyroidism: What's The Difference?
Though it's small, the thyroid is one of the most important glands in the body. It is responsible for producing hormones that regulate your metabolism and energy levels, according to WebMD. These hormones also help maintain body temperature and weight, and control menstrual cycles in women.
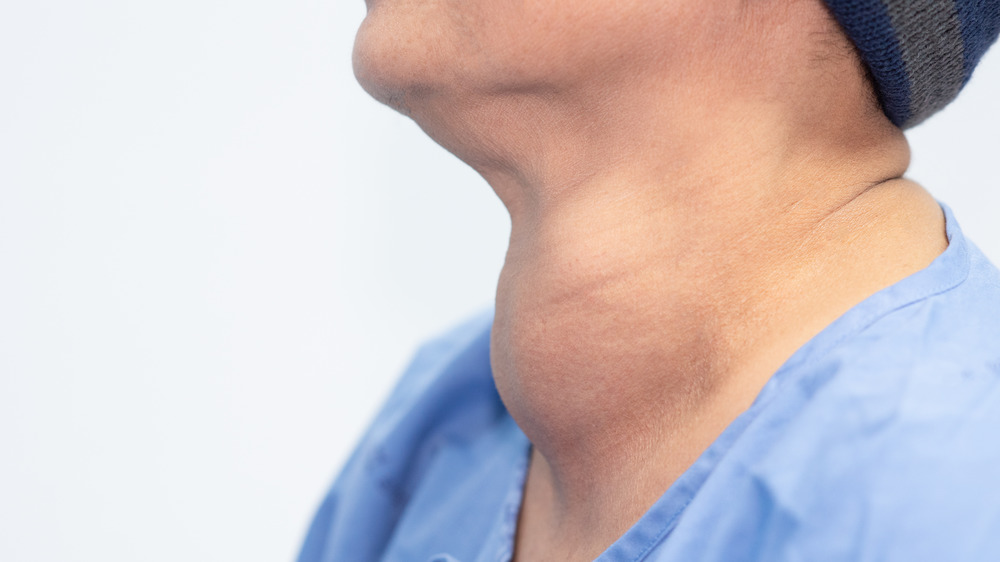
When the thyroid malfunctions it starts to produce too much or too little of certain hormones. These conditions are called hypothyroidism, in the case of too little, and hyperthyroidism, in the case of too much.
Health Digest spoke to Dr. Poonam Kapadia, an endocrinologist at Halifax Health, to learn more about how these conditions are similar and different. She said hypothyroidism is the most common disorder of the thyroid. "The thyroid's job is to make thyroid hormone. If the gland is underactive, it may not make enough. Thyroid hormones control how your body uses energy. They affect almost every organ in your body. When your thyroid doesn't make enough of these hormones, parts of your body slow down," said Dr. Kapadia.
By contrast, "Hyperthyroidism means your thyroid gland is too active. An overactive thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. This makes your metabolism work at a faster rate," she said.
What symptoms arise from each condition?
Symptoms are very different. With hypothyroidism, people present with dull facial expressions, fatigue, feeling cold, a hoarse voice, slowed speech, dry skin, weight gain, brittle nails, constipation, and more.
In the case of hyperthyroidism, people feel nervous or irritable, sweat more, have weak muscles and brittle hair, shaky hands, increased heart rate, high blood pressure, feel overly warm, and have weight loss. Both types of disorder will be diagnosed through a clinical exam, blood tests, and possibly imaging tests.
Treating the conditions is done a little differently, according to Kapadia. "For hypothyroidism, the goal of treatment is to return your level of thyroid hormone back to normal. You may need to take medicine that gives you a dose of thyroid hormones. This dose may need to be changed over time. You will likely need to take this medicine for the rest of your life. You will need follow-up blood tests to make sure you are taking the correct dose of thyroid hormone replacement," she said.
With hyperthyroidism, several medications may be used, including steroids, but treatment may also involve the use of radioactive iodine, or even surgery to remove the thyroid.
What causes hypo- or hyperthyroidism?
The two conditions have different origins, according to Kapadia. "The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disorder. This means your immune system starts to attack itself. It makes antibodies against the thyroid gland," she said. Hypothyroidism can also develop following pregnancy, she added. Causes of hyperthyroidism may include Graves disease, a toxic nodular goiter, or thyroiditis, a condition often caused by a virus.
Kapadia urges people to speak with their doctor is they are having unusual symptoms. "Thyroid disease is very common but requires the interpretation of the right laboratory and/or imaging tests when necessary. Most conditions can be easily treated, but it is imperative to follow up with your treating physician, take the prescribed medications and monitor your labs/symptoms carefully. Because some symptoms of thyroid dysfunction overlap with many other conditions, it is important to make sure the right diagnosis is made," she said.