Common Medications That Can Cause Anxiety
When we suffer from an ailment, whether something transient, such as a headache, or more chronic, like asthma, we trust that medication will help treat or cure whatever the ailment is. However, medications can come with side effects that can, at times, be just as troubling as the condition you're trying to treat. According to a 2013 study published by the AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings Archive, nearly 70% of drugs have anywhere from 10 to 100 side effects.
One of the potential side effects of your medication could be anxiety. While the Anxiety & Depression Association of America notes that nearly seven million adults suffer from Generalized Anxiety Disorder, one does not have to have anxiety to experience it as a side effect of medication. This is what is known as a substance-induced anxiety disorder, and it can be caused by the way the chemicals in your brain react to the medication you're taking (via Tufts Medical Center).
If you're experiencing symptoms of anxiety seemingly from out of nowhere, your medicine cabinet may be the first place you should check. These are a few medications that could be triggering anxious symptoms without you even realizing it.
Corticosteroids
An anti-inflammatory medication, corticosteroids can be used to treat a number of conditions, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and Chron's disease. They are very powerful medications, particularly when delivered in tablet form. Steroid tablets can impact the entire body, and caution should be exercised when prescribing or taking them, particularly when a person is suffering from any kind of mental health or behavioral issue.
Because corticosteroids can reduce gamma-aminobutyric acid, which is a neurotransmitter that regulates central nervous system activity, it can lead to a change in mood and anxiety. A 2023 study published in Cureus showed that some patients who had taken corticosteroids exhibited signs of depression, anxiety, panic disorder, and other mental health issues. For patients taking corticosteroids for more than 60 days, the study reported that 90% showed adverse effects. Similarly, a 2020 study published in Neuroendocrinology revealed that corticosteroid use was linked to a reduction in executive cognitive functioning and a greater likelihood of developing anxiety disorders.
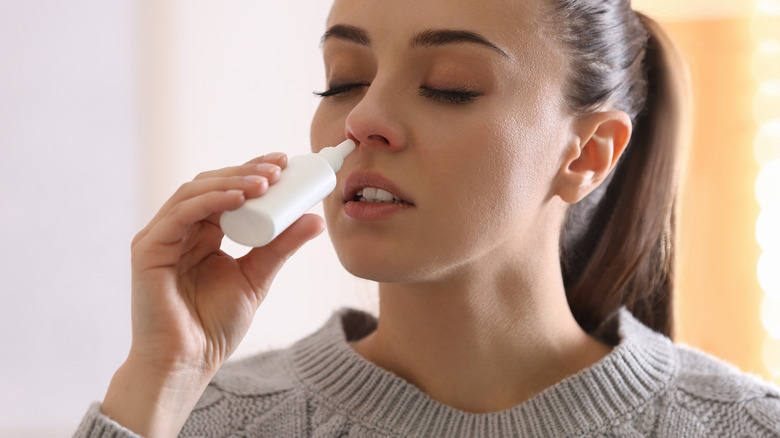
Decongestants
No one enjoys having a stuffy nose, either as the result of allergies, the flu, or even a common cold. When the nose is blocked up, nasal decongestants usually offer the first line of defense, offering a brief respite from the blockage and allowing you to breathe more freely. These decongestants reduce the swelling of the blood vessels and tissues in your nose, which opens the airways and relieves that stuffed-up feeling.
According to the Mayo Clinic, some of the ingredients in nasal decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine, can cause such symptoms as insomnia, tremors, and anxiety. A 2018 study published in the Journal of Undergraduate Neuroscience Education showed that the neurotransmitter responses to taking such stimulants as pseudoephedrine mimic the same responses generally associated with anxiety. In particular, pseudoephedrine increases the release of serotonin and dopamine in the brain. Having elevated levels of both of these neurotransmitters is also linked to anxiety.
ADHD medications
Stimulants such as Adderall change the chemicals in the brain to boost alertness and relieve the symptoms of ADHD. However, this chemical change can also produce anxiety, especially if the doses are not correct. While Adderall, for example, may not actually be the cause of your anxiety, it can cause such symptoms as higher blood pressure, raised heart rate, and insomnia. All of these conditions can increase anxiety or even induce a panic attack (via Everlast Recovery Center).
According to HealthMatch, Adderall can stimulate the amygdala, which is the part of the brain that reacts to danger. As a result, even if you are not in danger, this stimulation of the amygdala can trigger the fight-or-flight response in your brain, leading you to feel nervous, anxious, and tense. You could also feel physical symptoms such as hyperventilation, sweating, and trouble with concentration. If you're experiencing these kinds of symptoms while taking ADHD medication, it's a good idea to talk to your doctor. He or she can look into possibly prescribing an anti-anxiety medication to help balance out your symptoms.
Beta blockers
Usually used to treat high blood pressure, beta blockers work by suppressing the body's production of adrenaline, which causes the heart to beat slower (via the Mayo Clinic). In addition to hypertension, beta blockers can also treat other conditions such as arrhythmia, migraines, angina, and heart failure. Additionally, Calm Clinic notes that beta blockers could also increase the symptoms of anxiety. This is because the potential side effects of beta blockers, including shortness of breath, nightmares, and hallucinations, can cause panic in patients who already suffer from anxiety.
According to a 2021 study published in Hypertension, beta blockers have been linked to a variety of mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. These symptoms, among others, have been frequently listed as adverse reactions to these medications. Interestingly, however, beta blockers have also recently emerged as a possible treatment for anxiety in some cases, as reported by Texas Health. Because they block the production of adrenaline and slow the body's heart rate, beta blockers could be seen as a way to reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety and help to get the emotional effects under control as a result. However, this treatment may not be for everyone, and it's wise to discuss any anxiety treatment with your doctor to find the one that works best for you.
Medications with caffeine
Certain medications, such as those used to treat migraines, contain caffeine. Medications such as Excedrin, Anacin, and Darvon Compound all list caffeine as an active ingredient. This is partially because caffeine can affect the levels of a compound in the brain called adenosine. During migraine attacks, adenosine levels are known to rise, and caffeine can help reduce those levels and keep migraines at bay.
However, particularly for patients who are already prone to anxiety, caffeine can make things worse. A 2013 study published in General Hospital Psychiatry showed that, in patients with a preexisting panic disorder, doses of caffeine equivalent to five cups of coffee were enough to induce a panic attack. However, these attacks were not always exclusive to patients who already had a panic condition. The study also reported that healthy adults also saw an increase in anxiety after consuming caffeine. Additionally, caffeine can impact your sleep, which can make managing anxiety even more difficult. A 2014 study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry pointed to sleep problems as a red flag for anxiety disorders among young people.
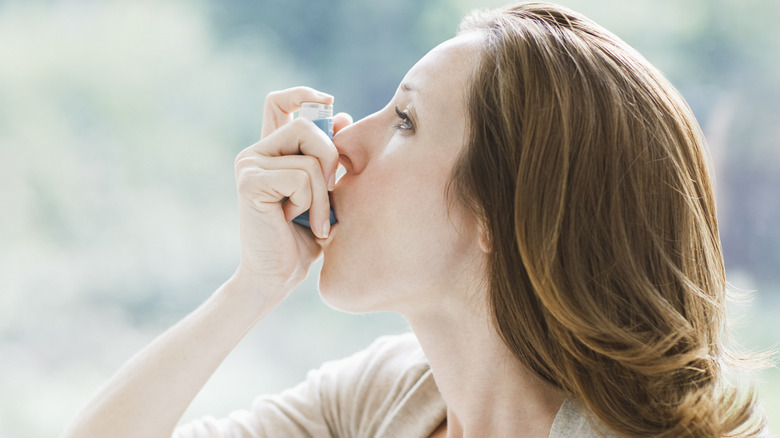
Rescue inhalers
For people who suffer from bronchial conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), inhaled medications such as albuterol can be a great source of relief. Albuterol causes constricted airways to relax and allow air to flow more freely to the lungs. However, for all of its benefits, albuterol can come with some side effects, including chest pain, increased heart rate, dizziness, and feeling nervous.
According to a 2022 article published in StatPearls, tremors and nervousness occurred in approximately one in every five patients who took albuterol. These tremors tend to be caused by albuterol's activation of the body's beta-2 receptor. This activation can trigger nerves in the body that control movement, resulting in shaking and tremors. K Health also notes that feelings of nervousness, agitation, increased excitability, and hyperactivity are all potential side effects of albuterol use, although they tend to be more common among children.
Antidepressants
Antidepressants known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) help to amplify the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain, regulating your mood and making you feel happier (via Medical News Today). However, in some cases, that boost of serotonin can cause anxiety levels to rise. A 2018 study published in Canadian Family Physician showed that, after starting an SSRI, the increase in serotonin levels could cause restlessness, irritability, and anxiety for anywhere from one to two weeks.
In some cases, those side effects can persist even beyond those initial two weeks, as evidenced by a 2014 study published by Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. According to that study, seven percent of patients continued to experience antidepressant-induced jitteriness and anxiety a month after beginning antidepressant treatment. Additionally, these patients also experienced a host of other side effects, including hostility, aggression, panic attacks, and trouble staying still. This condition is known as either jitteriness syndrome or activation syndrome.
Thyroid medications
If your thyroid gland is not producing enough thyroid hormone, it can lead to a condition known as hypothyroidism. When that happens, it can result in depression and anxiety. This is because the thyroid hormone plays a role in the regulation of such neurotransmitters as serotonin. When the thyroid isn't functioning properly, not only can serotonin production become low, it can also become irregular, leading to anxiety and panic attacks.
However, treating hypothyroidism can also come with its own set of troubling side effects (via Medline Plus). These can include anxiety, irritability, excessive sweating, and trouble falling asleep or staying asleep. According to a 2019 study published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, women who were treated with levothyroxine for hypothyroidism were more likely to experience anxiety and depression than women who did not have the condition. You should talk to your doctor before taking any medication for hypothyroidism to make sure that the medication and the dosage are right for you. They can check your blood regularly to keep an eye on your thyroid levels.
Anti-seizure medication
For patients who suffer from seizure disorders, medications such as phenytoin can be highly effective (via the Epilepsy Foundation). Phenytoin, which is also marketed as Dilantin, keeps the brain cells from firing too fast during a seizure, sometimes stopping them before they have even had a chance to begin. It can also be used in some cases to treat psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder. Because of its effectiveness and diverse uses, phenytoin is one of the most common anti-seizure medications currently on the market.
Despite its effectiveness, phenytoin has been reported to cause alterations in mood and cognitive problems. A 2012 study published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry reported a case of a 28-year-old male who displayed anxiety, aggression, and violent behavior. It was revealed that his phenytoin levels were very high and, over time, his symptoms improved greatly. It's also been reported that phenytoin can, in more serious cases, cause suicidal thoughts, increased depression, and potentially lead one to act on dangerous impulses (via Healthline). If you are taking phenytoin and experience any of these effects, you should call your doctor or 911 right away.