9 Habits Could Help You Live Decades Longer, According To Science
Abraham Lincoln famously quipped, "In the end, it's not the years in your life that count. It's the life in your years." While the quality of your years here on Earth likely matters to you, there are many people who also care about the quantity.
At the same time, people are becoming more concerned about how they will support themselves in retirement. For one, as life expectancy increases, they will have to stretch their savings while managing rising costs on a fixed income. Even so, CNBC reports that a 2022 study revealed that nearly seven in 10 people in the United States hope to live to 100. The study, which included 11,000 adults from Canada and the United States, also noted that the last 12 years of life are often impacted by illness, injury, or cognitive decline.
The good news is that there are preemptive steps you can take to not only extend your lifespan well before your golden years but also help you maintain optimal health.
If you're aiming to live for 100 years on the planet, the results of a recent American Society of Nutrition study involving 700,000 U.S. veterans revealed eight healthy lifestyle habits that can help you get there. Implementing all eight habits by the time you're 40 can extend your lifespan by 24 years, according to the study.
Even if you're past 40, it's not too late to take on healthy habits. And while cultivating eight habits to live longer is a great start — at Health Digest, we'll do you one better.
Get physically active
Many health experts say sitting for long periods can be as bad as smoking and can also shorten your lifespan, so if you're not one for exercise, the time is now to get physically active.
The results of 13 studies indicated that regular exercise increases life expectancy anywhere between 0.4 to 6.9 years, according to a paper published in Journal of Aging Research. Regular physical activity reduces the risk of developing a number of conditions that can lead to death, such as diabetes, heart disease, stroke, and cancer. By engaging in regular physical activity, you could lower the chances of developing one of these conditions by up to 35%. However, while the various study results were clear that regular physical activity helped to extend one's lifespan, more research is needed as to whether high-intensity exercise has an impact — positive or negative — on life expectancy.
So how much physical activity do you need to incorporate into your lifestyle to add on the years? While the Physical Activities Guidelines for Americans (2nd Edition) recommends between 150 and 300 minutes per week of moderate exercise or 75 to 150 minutes of intense exercise weekly for adults, a study of 116,221 adults revealed that more than the recommended amount will increase life expectancy by lowering the risk of death from cardiovascular disease, per the American Medical Association. Examples of moderate activity include walking, weightlifting, and lower-intensity exercise. Running, biking, and swimming fall into the category of vigorous exercise.
Avoid addictive drugs
One bad habit guaranteed to take years out of a lifespan is drug abuse. Avoiding drug addiction will have many benefits that will also help you live a healthier life day to day.
Besides losing actual time during your life by using drugs, whenever you use drugs or alcohol, you are reducing your life by hours each time, according to the experts at Narconon. They point to a tool called the Omni Calculator, which can show you how much of your life you lose by taking certain drugs or drinking alcohol. For instance, taking cocaine once already reduces one's lifespan by 6.6 hours. One experience with methamphetamine takes 9.2 hours off your life; using heroin reduces one's life by a full day.
Using addictive drugs also reduces the quality of your life. The team at Clean Recovery Centers reports that taking methamphetamine ruins your teeth. Additionally, cocaine users may experience convulsions, and marijuana smokers are likely to irritate their respiratory tract.
The generation into which one was born and how drugs fit into that will also play a role in life expectancy, with members of Gen X identified as the generation to most likely die from drug overdoses. Millennials are falling victim to opioids, part of what has led to their declining life expectancy of 78.6 years. The Boomer and Gen X generations have an average life expectancy of 84.5 and 78.7 years respectively.
If you or anyone you know needs help with addiction issues, help is available. Visit the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration website or contact SAMHSA's National Helpline at 1-800-662-HELP (4357).
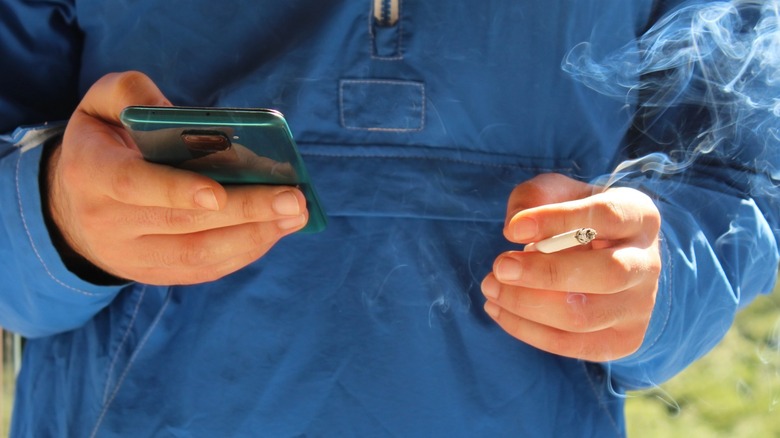
Stop smoking
It likely comes as no surprise that health experts across the spectrum strongly advise against smoking. Not only does smoking work against promoting a longer lifespan, but roughly one in five deaths in the United States is due to cigarette smoking annually, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Some 480,000 people die in relation to smoking every year, including those exposed to secondhand smoke. American adults who smoke have a mortality rate that is three times higher than non-smokers, as smokers are more at risk of developing cancer, respiratory disease, and vascular disease.
In fact, smokers can lose up to 10 years of their lifespan, according to a 2013 United Kingdom study published in Elsevier that followed one million women in the UK. Quitting smoking by age 40 can help prevent 90% of the increased mortality risk; ceasing smoking by the age of 30 can prevent over 97%. However, it is never too late to quit. The experts at Healthline report that quitting smoking in your 60s can add roughly 3.7 years to your life, and ceasing smoking in your 80s may still support improved health outcomes.
Quitting smoking does more than simply increase your lifespan. It improves your quality of life immediately, the American Cancer Society states that you will notice the effects immediately. For one, within minutes of quitting, you will experience a lower heart rate and blood pressure, and within a few weeks, your lung function and circulation will improve.
Manage stress
Experiencing some amount of stress can be good for you. For example, short-term stress can be a motivator to help you achieve your goals.
However, there comes a point when stress becomes unhealthy. For one, too much stress can lead to anxiety, depression, gastrointestinal issues, and an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease. All of these conditions have the potential to accelerate aging, lead to premature death, and shorten your lifespan, per University of Massachusetts Global.
Additionally, the Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion reports that high amounts of stress on a consistent basis can lead to other dangerous health conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, and a weakened immune system, all of which can potentially put you at a higher risk for a shorter lifespan. Physical signs that you are experiencing stress can include headaches, sleeping issues, gastrointestinal problems, weight gain or loss, and muscle tension.
Common stressors such as squeezing in a lot in too little time, work challenges, money issues, dealing with a long-term illness, or providing supportive care for a sick loved one can lead your body to release stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. However, how you manage stress, especially chronic bad stress, is key to promoting your well-being. The experts at Summa Health suggest strategies, such as incorporating meditation techniques into your daily routine and accepting events that are out of your control, as ways to manage stress and improve your quality of life.
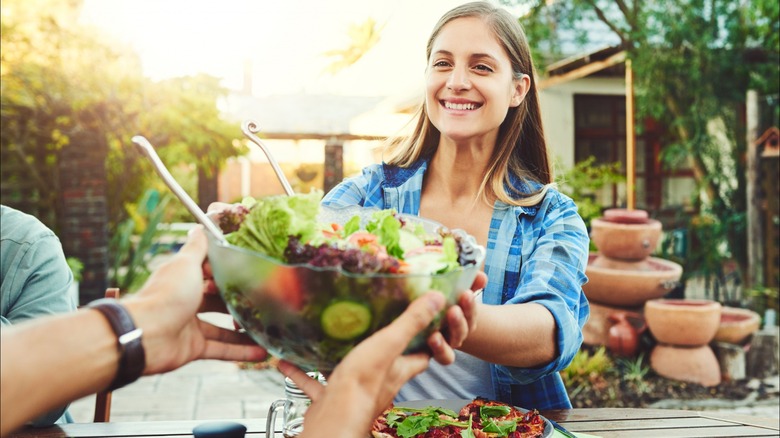
Maintain a healthy diet
Improve your diet, and you may be able to extend your life by a decade, according to the experts at Medical News Today. A free online calculator called Food4HealthyLife, which researchers developed in association with a study that examined the typical Western diet and the optimal diet, can help users determine how adding certain food groups into their daily meal plan can potentially extend their lifespan. Because your potential longevity goes beyond your diet, the calculator also includes other factors such as age and gender.
Since switching to the optimal diet may be too big of a leap for many people to make, the calculator suggests the optimal diet as well as what the calculator's creators dub a feasible diet, which resembles more familiar diets but also includes clear benefits. Kristin Kirkpatrick, a dietitian at Cleveland Clinic who was not involved in the study, told Medical News Today that taking baby steps can often be a good approach to transition to the optimal diet.
So what are some foods that you might want to swap into your diet to add on those extra years? Health experts tell Forbes Health that eating foods that are part of a plant-based diet, which is rich in essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, is an excellent wayto increase your longevity. Consuming fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, which are the foundation of a plant-based diet, has been linked to a reduced risk of developing adverse health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers, among other serious health problems.
Consume alcohol in moderation – or not all
It seems every year or so, one study says drinking alcohol in moderation is safe and may even help improve heart health and, consequently, life expectancy, per Time. Then, another study advises against consuming alcohol. So what's the best habit in this situation?
A study published in Nature in 2022 suggested that moderate drinking could lead to a better survival rate compared to non-drinkers, despite the complicated and controversial association that alcohol has with health outcomes. The study included 430,016 adults who were part of a health-screening program that began in 1994. Moderate drinkers (those who consumed no more than one drink per day) experienced notable benefits and stood to potentially add nearly one year to their life expectancy. Meanwhile, those who consumed alcohol beyond this limit faced a loss of close to seven years. This loss surpassed 10 years for individuals who combined excessive drinking with smoking.
Other research revealed 140,000 people died annually between 2015 and 2019 due to excessive alcohol use, and many experts state that moderate drinking on a regular basis also poses risks. Scientists believe that alcohol consumption has a hand in altering your DNA, which can lead to malignant tumor growth and also cause tissue damage, per the New York Times. Despite the potential risks, Dr. Tim Naimi, director of the University of Victoria's Canadian Institute for Substance Use Research says that if you are a drinker, even a slight reduction can yield benefits, particularly if your current alcohol consumption surpasses recommended guidelines. The risks escalate markedly once consumption exceeds a couple of drinks daily.
Stick to a smart sleep routine
Though it may seem like a passive state, a lot is happening while you sleep. A good night's sleep gives your body time to rest and restore. Bad sleep hygiene can ultimately lead to heart and brain health issues.
If adding at least two and a half years to your lifespan sounds good to you, you may want to follow all the strategies based on a recent study that involved 172,000 participants who responded to sleep questionnaires between 2013 and 2018 as part of an annual survey coordinated by the CDC and National Center for Health Statistics.
CNN reports that these strategies include getting seven or eight hours of restful, uninterrupted sleep every night at least five times per week on a consistent basis, sticking to a sleep routine as you prepare for bed, curtailing booze-drinking well before bedtime, avoiding blue light and screens, and making your environment conducive to sleep.
Study co-author Dr. Frank Qian, a clinical fellow in medicine at Harvard Medical School and internal medicine resident physician at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, stated that if you can commit to incorporating these habits, the chances of adding years to your lifespan will increase.
To optimize your sleep environment, make sure your space is cool, dark, and quiet, and consider practicing meditation, gentle yoga poses, or taking a warm bath before bed to help build a relaxing nighttime routine that sets you up for a solid night's rest, per CNN.
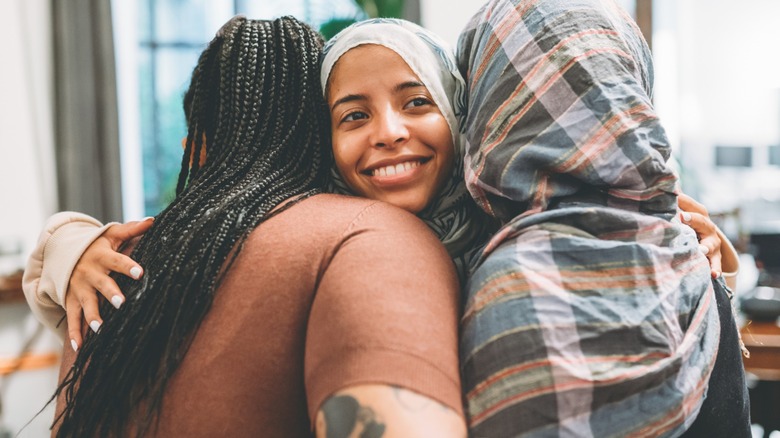
Create positive social relationships
It can be hard for some people to maintain strong social ties, especially as we age. But social connections are essential for mental health and brain function. Strong social ties can also help you live longer.
Results of a well-known study out of Harvard that originated in 1938 and spanned over eight decades concluded that strong social ties and positive relationships will help you live longer, happier lives. CNBC reports that assessing your "social fitness" by taking stock of your connections and leaning into relationships that help you thrive is essential.
A 2004 study revealed more evidence linking the strength of social connections and extended lifespan by uncovering areas in the world where people tended to live longer. The five locations where researchers determined people lived higher quality and longer lives were labeled "blue zones." The study found that people in these areas had lower rates of serious diseases and were 10 times more likely to live to 100 compared to those living in the United States. The five areas are Ikaria, Greece, Okinawa, Japan, Sardinia, Italy, Loma Linda, California, and Nicoya, Costa Rica.
One of the traits of those living in blue zones that leads to longer, happier lives is being part of supportive social circles. However, you don't have to live in a blue zone to improve your lifespan.
Taking stock of relationships, determining what areas of your life need more of a sense of connection, and reaching out to people in your life to foster deeper relationships can put you on the path to deepening your social ties, per CNBC.
Cut down on screen time
Too much sitting and screen time can lead to adverse health consequences that can shorten your lifespan. The New York Times reports that constant engagement with smartphones raises your cortisol, the body's primary "fight-or-flight" stress hormone, spiking your blood pressure, blood sugar, and heart rate. By increasing your cortisol levels on a continuous basis by regularly looking at your phone screen, you are putting yourself at risk of decreasing your lifespan, as constantly raised stress levels can often lead to serious health issues.
Additionally, despite technological advancement in medicine improving life expectancy, technology has also led to increased sedentary behavior, creating a greater risk of developing obesity as well as diabetes, joint problems, high blood pressure, and heart disease, according to the experts at Jai Medical Systems. Between being entranced with news, social media, and email, Americans spend an average of four hours daily sitting and staring at their phone screens, per New York Times.
So why are we so connected to our phones if they cause stress? The answer is dopamine. Your phones and apps are specifically designed to trigger the release of dopamine, a chemical that leads to the formation of habits and addiction behaviors. Consequently, these dopamine hits hinder you from taking your eyes off your phone.
For a healthier lifestyle — and to promote a longer lifespan — devote some of those sedentary, stress-inducing, phone-staring hours instead to reading a physical book, taking up a hobby, or meeting up with friends.