Things That Can Cause Your Mouth To Water Abnormally
You've been noticing that your mouth has been watering a lot lately. While it's normal for your mouth to water, it seems like it's been excessive to where you're carrying a tissue with you, just in case. Excessive saliva is called hypersalivation or ptyalism, and it can be a rather uncomfortable condition. To put it simply, hypersalivation is when your mouth produces excessive saliva or saliva isn't being appropriately swallowed, leading to drooling.
Common causes of too much saliva might have something to do with the pain in the mouth, sinuses, and throat from sinus or throat infections, cavities, inflammation, ulcers in the mouth, false teeth, poor oral hygiene, and jaw dislocation, according to Medical News Today. But these aren't the only reasons your mouth might be watering abnormally. Hypersalivation can come from disorders beyond the pain in the mouth, like your GERD, pregnancy, toxins, or even specific medications. Those with neurological disorders can even experience sialorrhea or constant hypersalivation.
Get in-depth information on a few chronic and temporary conditions that might leave your mouth watering abnormally. Dive into the details of how you might relieve this irritating condition.
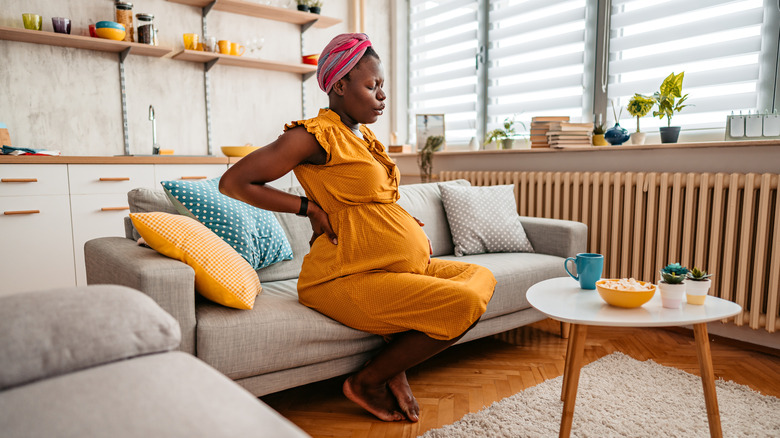
Pregnancy and morning sickness lead to abnormal saliva production
Pregnancy can also come with a few not-so-fun symptoms. Hormones wreak havoc on the body as it changes for the growing fetus. And morning sickness and nausea are very common, which can cause a pregnant individual to feel their mouth watering more than usual. When your body feels nauseous, its first response is to create more saliva. Dr. Isaac Eliaz told NBC News, "Our digestive process starts in the mouth with the saliva, which is high in amylase, an important digestive enzyme that helps break down carbohydrates. So as part of the digestive process triggered by whatever may be causing the nausea, we have increased salivation."
Hormones from pregnancy can also cause the person to experience abnormal salivation that leads to nausea and sickness, creating a vicious cycle (via NCT). This is especially true for those who experience hyperemesis gravidarum, an extreme morning sickness. Parents with this condition typically experience severe nausea, dehydration, dizziness, and weight loss, according to Cleveland Clinic. Extreme cases can even lead to malnourishment and hospitalization, depending on the severity.
Abnormal mouthwatering can be harder to treat during pregnancy. However, you can try eating small meals and taking sips of water to wash the saliva down. It can also be helpful to suck on candy or brush your teeth for saliva with a taste or thicker consistency.
Water brash from gastrointestinal reflux disorder (GERD)
Having your mouth watering all the time can be hard enough to deal with on its own, but those with GERD have a double whammy. GERD is a disorder where stomach acid flows into your esophagus. This creates a range of symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and trouble swallowing, stated Mayo Clinic. In addition to indigestion, GERD sufferers can also experience a condition known as water brash.
This symptom of GERD causes the mouth to create too much saliva, which then combines with stomach acid. This acidic saliva leaves you with heartburn and a sour taste in your mouth (via WebMD). It's also noted that excess saliva causing water brash could be the body's response to the excess stomach acid irritating the esophagus. This condition can often be confused with regurgitation, but the excess saliva differentiates the two. While water brash is an uncommon condition, it can leave those who experience it feeling uncomfortable.
Hypersalivation due to water brash can be a chronic condition depending on your GERD treatment. The first line of defense against water brash is making specific lifestyle changes like removing fatty foods, losing weight, eating small meals, avoiding alcohol, and quitting smoking, according to Healthline. Depending on your healthcare specialists' recommendations, you might also need to take medications designed to reduce stomach acid, like Prilosec or Nexium.
Hypersalivation as a medication side effect
Many drugs have different side effects — but ideally, the side effects are minimal compared to the benefits of the treatment. This statement is true of many medications. But specific medications used to treat psychosis and dementia can trigger watering as a side effect.
According to a 2005 study in Drugs of Today, clozapine is a common drug that can lead to drooling, either from producing too much saliva or limiting the ability to swallow. According to the National Library of Medicine, clozapine is the first line of defense for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. It has the advantages of lowering suicide, improving cognition, and decreasing relapse. It can also lead to excessive saliva and an increased risk of aspiration pneumonia.
Another common drug that could cause hypersalivation symptoms is cholinergic agonists, which are used to treat Alzheimer's symptoms. According to a 2018 Brain study, cholinergic therapy inhibits acetylcholine breakdown and improves cognition and global functions. While the side effects can be annoying, healthcare professionals can often prescribe other medications that limit the production of saliva.
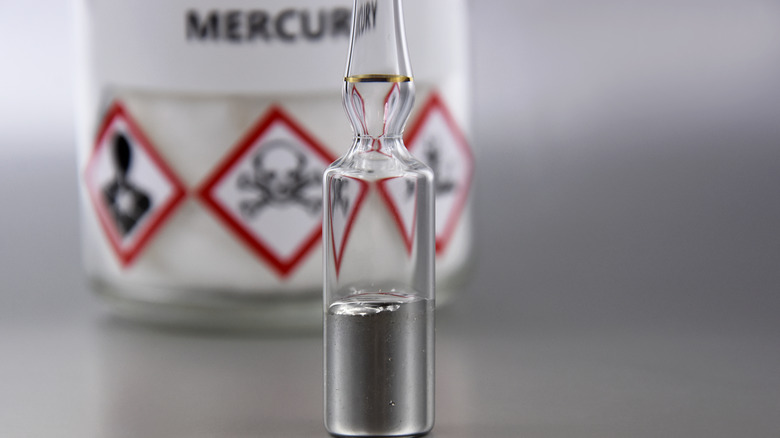
Toxins and poisons lead to abnormal mouth watering
When you think of accidental poisoning, you might think of taking too much or the wrong medication. It might also make you think of your child entering your cleaning cabinet. But accidental poisoning can come from some unknown areas. For example, people working on farms can get too much exposure to herbicides or insecticides, leading to poisoning and mouthwatering, according to the DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.
It's also common for adults and children to accidentally get mercury poisoning from overeating large fish, broken light bulbs, and batteries. Beyond hypersalivation, mercury poisoning symptoms include headaches, emotional changes, mental problems, and skin conditions. Diagnosis is essential to get treatment and reduce the mercury in your system. Additionally, the poison from scorpion bites and specific stings can lead to excessive drooling and require emergency medical attention (via the University of New Mexico College of Pharmacology). Other symptoms to watch out for include bite marks, numbness and tingling, and trouble breathing.
Since drooling or excess saliva can come from several different sources, it's essential to limit exposure to heavy metals and toxins by following proper safety procedures like gloves and masks. You'll also want to shake out any shoes or bedding, especially if you live in an area with poisonous insects.
Neurological disorders are linked to abnormal mouthwatering
Many neurological disorders can have devastating effects on the body, like taking away muscle control and limiting the ability of the body to function in a specific area. Dr. Steven Bachrach, M.D. told Brain & Life, "Any condition that affects the muscles and nerves of the bulbar area (the swallowing mechanism) could cause increased drooling." Therefore, people with conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease, and cerebral palsy symptoms can have issues swallowing saliva. This leads to excess drooling (via Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders).
Since drooling is typically caused by a lack of muscle control, many healthcare providers try to use a combination of medication and therapies to help to alleviate the symptoms, which can affect the daily life of the individual. Additionally, posture, dietary changes, and behavior modification might be worth trying before moving on to more invasive therapies, like surgery.
If you have pain in your mouth or nasal cavity, you might expect to have your mouth watering abnormally until the condition is alleviated. However, excessive drooling and hypersalivation symptoms can become a chronic condition that needs diagnosis and treatment.