How To Tell The Difference Between A UTI And Bladder Infection
It usually starts off with a little more urgency than usual. Perhaps you find yourself hustling to the bathroom a little faster than you normally would. Once the toilet is in view, you can't pull your pants down fast enough! But — not to worry — you made it, and now sweet relief is yours. But wait! Instead of relief, you're met with a painful burning sensation...
Anyone who's had to endure a urinary tract infection (UTI) once or twice can spot the uncomfortable symptoms from a mile away. A common bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract, UTIs occur when bacteria — usually originating from the skin or the anus — find their way into the urethra (per Mayo Clinic). While UTIs have the ability to make their way from the urethra all the way to the ureters, bladder, and kidneys, they most commonly cause disturbances in the urethra and the bladder. And while bladder infections are a type of urinary tract infection, not all UTIs include the bladder. So how can you tell if what you're dealing with is an infection of the lower urinary tract or if it's made its way up to your bladder? Let's find out.
The differences between a bladder infection and other UTIs
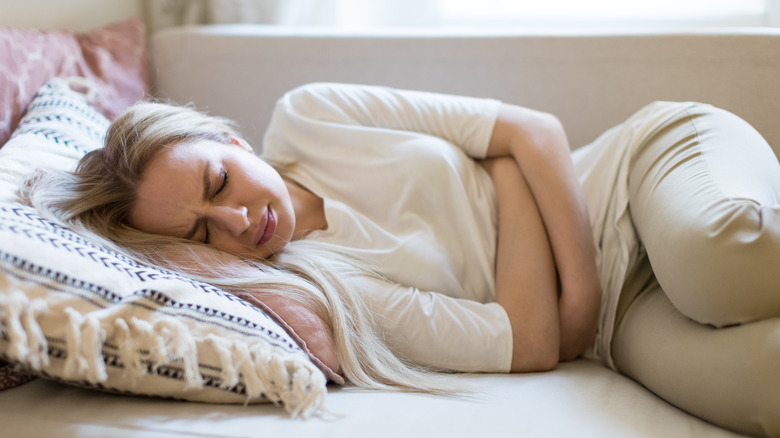
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) points out that bladder infections are the most common type of UTI. If you're dealing with a bladder infection, you may experience symptoms like painful urination, a persistent feeling like you need to pee, the inability to produce more than a few drops of urine, discomfort in the stomach or pelvis, and urine that has a cloudy appearance and a foul odor.
Because bladder infections share many symptoms with UTIs affecting other parts of the urinary tract, differentiating between the two can prove to be difficult (via Medical News Today). If what you are experiencing is an infection in the urethra that hasn't yet made its way up to your bladder, you will likely be able to tell the difference because you'll feel pain and burning during urination — and might even notice some discharge coming from the urethra when you use the bathroom — however, you will experience a noticeable absence of pain surrounding the bladder and abdomen.
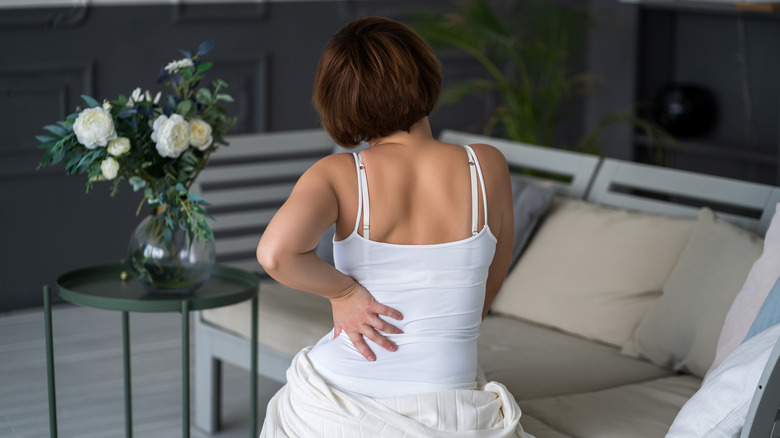
The most serious kind of UTI you can have is one that affects the kidneys. Once a UTI has reached your kidneys, you may experience all the same symptoms of a bladder infection with the addition of symptoms like fever, chills, and lower back pain.
Treatment options
When you're in the throes of a UTI, seeking treatment is your best bet for getting rid of those disruptive symptoms fast. How your UTI is treated usually depends on the severity of your infection. Healthline explains that healthcare professionals categorize the severity of UTIs as either "simple" or "complicated". Most UTIs that affect the lower urinary tract and bladder are considered simple infections. These usually require taking an antibiotic like trimethoprim, ciprofloxacin, and amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium for three to five days. However, some bladder infections may have progressed to the point of being a complicated infection, in which case a longer round of antibiotics — typically lasting for 14 days — may be necessary (per Health).
Infections that reach the upper urinary tract and kidneys are usually considered complicated, and thus harder to treat (per Healthline). In some cases, kidney infections may require a visit to the hospital for intravenous antibiotics and fluids.