Signs Your Cortisol Levels Are Low
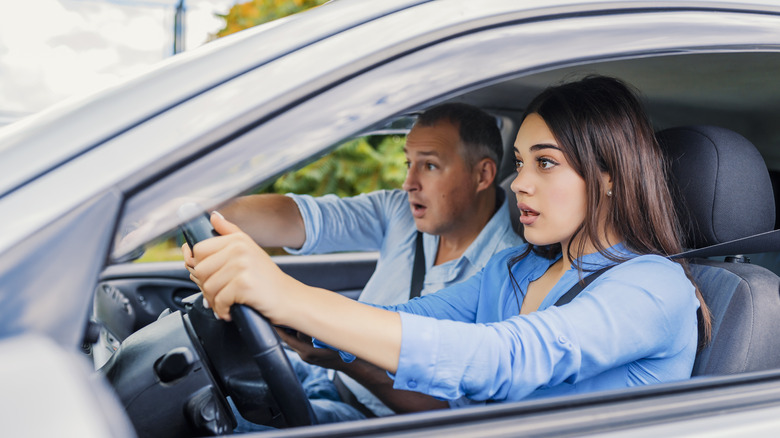
Most people have been in a situation where, all of a sudden, something in the environment captures their attention immediately. Maybe you are out in nature and see a large wild animal, or are crossing the street and see a car speeding toward you out of nowhere. Your heart starts to race, your vision narrows, your attention focuses intensely on the moment, and your body feels ready to spring into action. This is known as the classic fight or flight response. It is an evolutionary survival response that prepares the body for action. One of the biochemicals that drives the fight or flight response is cortisol, a steroid hormone. But cortisol is a complex hormone — it is not a one-trick pony. Cortisol plays a role in the regulation of metabolism and blood pressure, among other things (via the University of Utah Health)
In some cases, people can have excessive amounts of cortisol in their bodies, otherwise known as Cushing's syndrome. If left untreated, Cushing's syndrome can lead to infections, blood clots, and even a heart attack. If having too much cortisol can cause health issues, you might wonder what happens when the body has too little cortisol. Here's everything you need to know.
Addison's disease
Addison's disease is a type of long-term autoimmune response that occurs when the body's adrenal glands produce insufficient amounts of the hormones aldosterone and cortisol, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Notably, people with existing autoimmune diseases, like Type 1 diabetes, have a greater risk of developing Addison's disease.
There are various signs and symptoms of Addison's disease. For example, you may feel more tired progressively over time. Other symptoms can include desires for salty food, mood swings, dehydration, diarrhea, low blood sugar, low blood pressure, minimal appetite, pain in the abdomen, areas of dark skin around existing bodily scars, and even muscle and joint pain. In more extreme cases, symptoms of Addison's disease can have a rapid onset and the results can be life threatening. If you experience low blood pressure, loss of consciousness, severe diarrhea and vomiting, severe weakness, or extreme pain in your lower back, legs, or belly, then you may be experiencing an addisonian crisis.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, or think that you may be having an addisonian crisis, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Treatments for Addison's disease
Addison's disease is not curable, but you can treat the disease and still live a healthy life (via Cleveland Clinic). Notably, since Addison's disease is a long-term or chronic condition, medication is needed for your entire life. But everyone is different, so the amount of medicine you may have to take can vary. The quantity can also change based on factors like infection, trauma, and stress to help reduce the odds of a sudden adrenal crisis.
The primary treatment for Addison's disease involves receiving injections of the hormones aldosterone and cortisol that you are low in. However, you will receive synthetic versions of the hormones. Your doctor may recommend taking the drug fludrocortisone to replace aldosterone. On the other hand, the drug hydrocortisone is used to replace cortisol.
All in all, you can speak with your doctor about carrying a shot of cortisol on your person for emergency use.