What Is A DEXA Scan?
A Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) scan is a medical imaging test that measures the body's bone mineral density (BMD). It is an important measure of overall bone health and is used to assess the risk of developing conditions such as osteoporosis, per the National Council On Aging (NCOA). Bone density refers to the number of minerals — primarily calcium — found in bones. As we age, our bones naturally lose density and become weaker. This can lead to an increased risk of fractures and other bone-related injuries, explains the NCOA. Low bone density, also known as osteopenia, affects about 34 million American adults, per the Cleveland Clinic.
Having good bone density is important because it ensures that bones are strong and able to withstand stress and pressure. High bone density protects against fractures and other bone-related conditions like osteoporosis, which can be painful and debilitating. This often results in a decrease in quality of life, per the NCOA.
In addition to helping prevent fractures and other injuries, bone density plays a critical role in maintaining the structure and stability of the body, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Strong bones help protect essential organs from injury and are an indicator of good physical health.
How does a DEXA scan work?
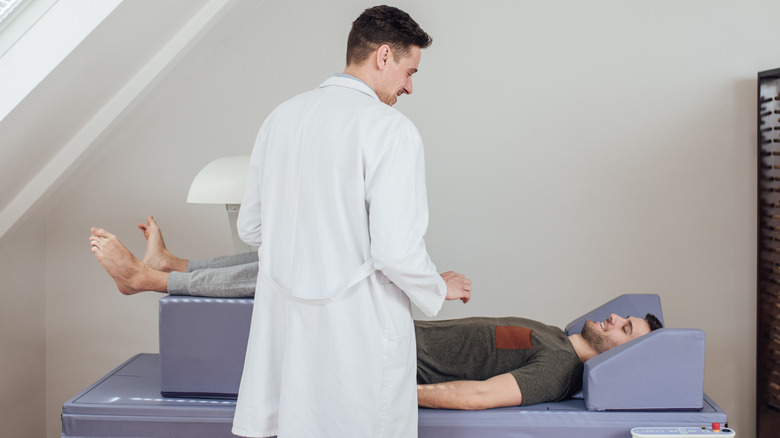
A DEXA scan is performed using a specialized X-ray machine that emits beams of X-rays that penetrate the body. They are absorbed by different tissues, including bone and fat, says the National Health Service (NHS). The machine measures how many X-rays the bones absorb, and the information is used to calculate the BMD.
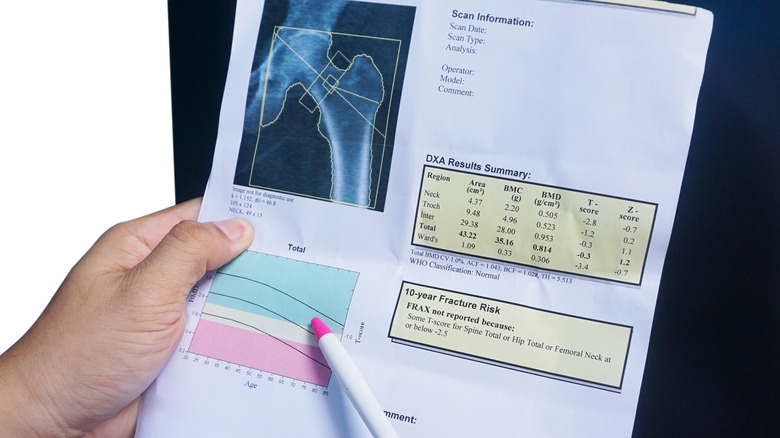
According to the NHS, the results of a DEXA scan are often reported as a T-score and a Z-score. The T-score compares your BMD with that of a healthy young adult of the same gender, while the Z-score compares your BMD with the average BMD of people of the same age.
A DEXA scan is often recommended for people aged 65 and over and those with a family history of osteoporosis, says the Cleveland Clinic. The scan usually takes around 10 to 20 minutes and is performed while the patient lies flat on their back — patients can remain fully clothed throughout the process, according to the NHS.
Is a DEXA scan safe?
According to the NHS, the DEXA scan is painless. More so, it is considered safe — it uses low-dose X-rays and a very small amount of radiation compared to other medical imaging tests, such as CT scans, per an article updated in 2022 in StatPearls. According to the study, the test is an effective tool for diagnosing osteoporosis and monitoring its progression. It can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for the condition. A DEXA scan can monitor calcium and vitamin D levels, as well as the effectiveness of bone-strengthening medications.
Although safe, keep in mind that all X-rays generally involve exposure to ionizing radiation. This can be harmful in large doses and contribute to diseases like cancer, according to the American Cancer Society. People who suspect they may be pregnant should inform their doctor before undergoing a DEXA scan as a precaution. According to the NHS, the scan isn't recommended for pregnant people.