The Types Of Doctors You Need To See To Treat Autoimmune Diseases
The immune system, which is made up of a large network of cells, organs, proteins, and tissues, is the body's preventive mechanism against infections, viruses, and parasites (via Medical News Today). When unwanted substances enter the body, it mounts an immune response while playing an active role in the optimum functioning of your body. However, health conditions can arise when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in your body. This is known as an autoimmune disease (via WebMD).
Over 100 autoimmune disorders exist, including lupus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Autoimmune diseases affect about 23.5 million Americans, and nearly 80% are women (per Johns Hopkins Medicine). The exact cause of the condition is unknown — however, certain viruses, chemicals, and environmental factors might confuse the immune system, causing it to attack itself, per Medline Plus. The symptoms may vary based on the autoimmune condition, but common ones include fatigue, fever, swollen glands, and shortness of breath (per the Cleveland Clinic).
Research efforts are still underway to gain more insight into treating autoimmune diseases. There's currently no known cure, and treatments often focus on reducing symptoms. As autoimmune diseases vary, knowing the type of doctor to see is equally important. In other words, seeking a doctor with greater awareness of your condition can speed up diagnoses and treatment.
Dermatologist
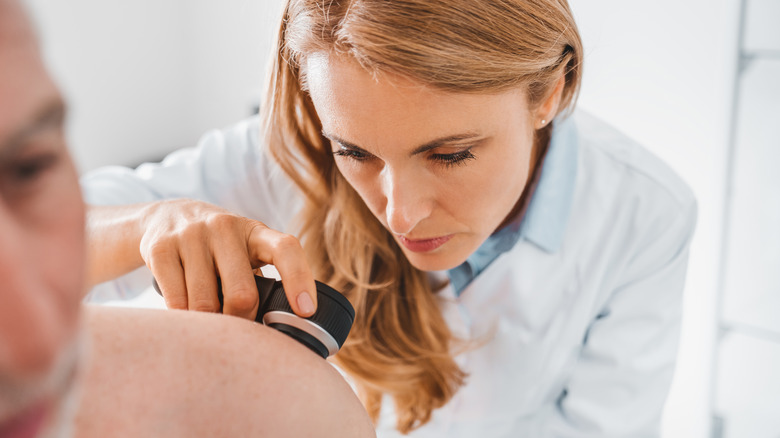
The symptoms of autoimmune skin diseases often include skin-related conditions, such as rashes, blisters, lesions, and scaly patches (per the University of Utah Health). Some common autoimmune conditions that affect the skin include dermatitis herpetiformis and lupus. Akin to other autoimmune diseases, there's no known cure for conditions that affect the skin. However, several treatment options exist to prevent flare-ups and other complications. That's where a dermatologist comes in handy.
A dermatologist is a medical doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating various conditions that affect the skin, hair, and nails (via WebMD). Apart from diagnosing autoimmune skin conditions, a certified dermatologist can create an effective treatment plan comprising medications, like corticosteroid or antimalarial, if you have an autoimmune skin disorder, like lupus (per the American Academy of Dermatology Association). However, your dermatologist may consider alternative treatment options, such as laser therapy, if symptoms persist after medications. For this reason, you may see your dermatologist more frequently. Overall, it's best to see a dermatologist once every three or six months, depending on how severe your autoimmune skin disorder is.
Rheumatologist
About 1.5 million people have rheumatoid arthritis, and this autoimmune condition is more common in women than men (via the Arthritis Foundation). Rheumatoid arthritis isn't fatal, but the condition can make you vulnerable to physical complications that can compromise your overall health and affect your life span, explains Medical News Today. One example is joint damage, which is present in 80% to 85% of people with the condition (via Johns Hopkins Medicine).
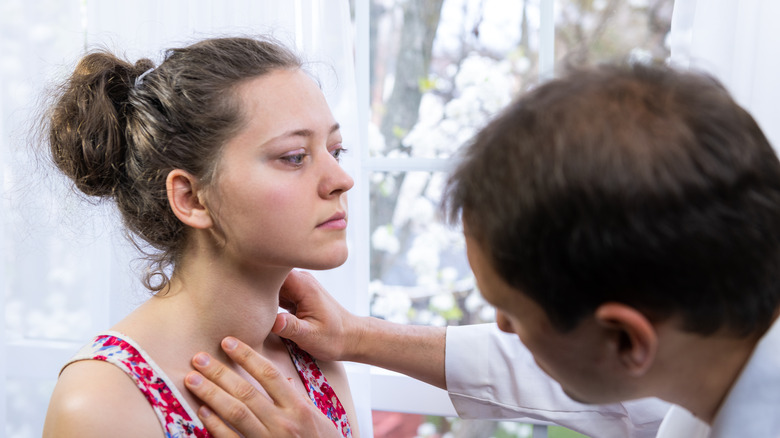
The condition can be hard to diagnose during its early stages, but it's crucial to seek early care from a rheumatologist (via WebMD). A rheumatologist is an internal medicine doctor, who deals with arthritis and other autoimmune systemic diseases causing the joints, muscles, and bones to swell.
According to the American College of Rheumatology, a rheumatologist has the requisite training to treat autoimmune diseases. After diagnosis, rheumatologists can help recommend drugs that boost the immune system and biologic therapies to help alleviate the diseases. At times, they do suggest oral medications, like steroids, if your autoimmune condition requires treatment. Keep in mind, these medications can have several effects, from changing the course of the disease over time to infection.
Endocrinologists
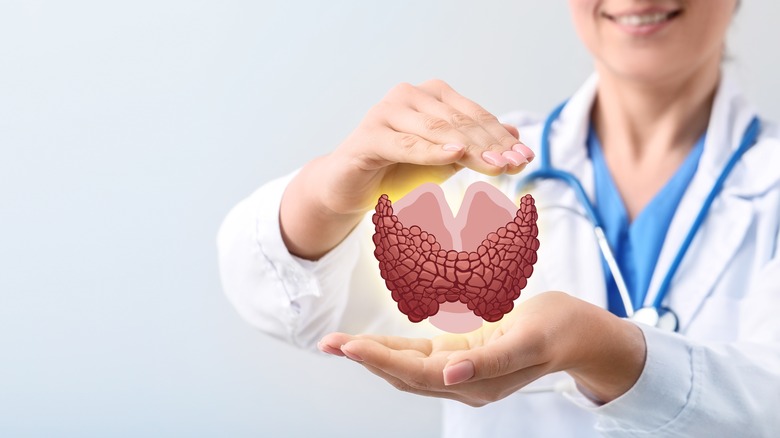
Endocrinology deals with the endocrine system and its hormones, as per the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE). The endocrine system plays an important role in your body. It comprises glands and organs that release up to about 40 hormones to support numerous functions, including blood sugar control, metabolism, heart regulation, and sexual development and function.
A 2018 study published in the journal, Minerva Endocrinologica, identifies several autoimmune diseases that can affect the endocrine system, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease, which are the most common. However, other conditions, like hypophysitis and adrenalitis, can also affect the endocrine system, even though they're rare. Endocrinologists can help with the diagnosis and treatment of health conditions related to the body's hormones, hormonal glands, and tissues, which comprise the endocrine system, per WebMD. However, in some cases, you may see an endocrinologist in an outpatient setting after a referral from your primary healthcare provider has been issued.
Immunologists
Immunology is the study of all aspects of the immune system, from its structure and function to the several disorders that can affect the immune system (via The American Association of Immunologists). An immunologist can work in various settings. While some are based in labs, others work as clinicians helping patients diagnose and manage autoimmune diseases.
After physically examining you and assessing your medical history, immunologists run tests to diagnose autoimmune diseases (via WebMD). They usually create an effective treatment plan based on your test results. You might need to see an immunologist if you have autoimmune conditions, like multiple sclerosis or lupus. However, in some instances, you might be referred to a rheumatologist.
The differences between these specialists aren't much, but some deal directly with autoimmune disorders more than others. Immunologists treat conditions affecting the immune system, while rheumatologists specialize in the musculoskeletal system, according to Healthline. Regarding autoimmune diseases, immunologists can recognize the symptoms, but rheumatologists are usually the best option for effective diagnosis and treatment.
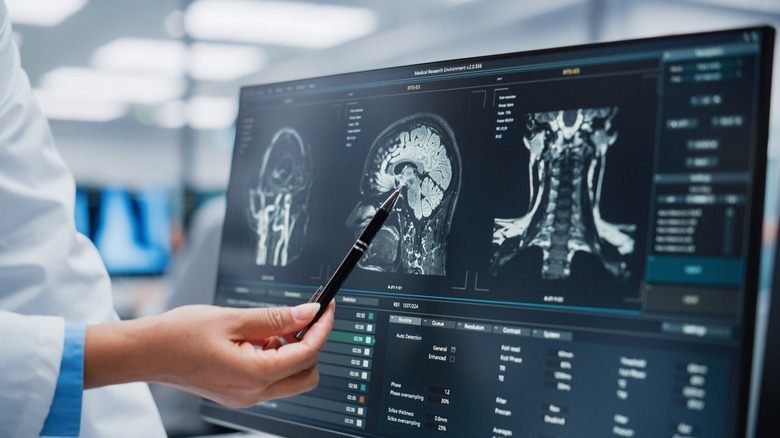
Neurologists
Neurology is a branch of medicine that deals with the nervous system (via the University of Rochester Medical Center). Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, according to Mayo Clinic. Keep in mind, clinical presentations can become complex, and other conditions may be mistaken for autoimmune nervous disorders. Therefore, autoimmune neurological disorders require expert evaluation to present an accurate diagnosis. That's where neurologists come in handy. Neurologists can diagnose and prescribe treatments for symptoms of neurologic autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis can range from blurred vision, difficulty walking, muscle weakness and spasms, and problems with balance and coordination, according to the National Health Service (NHS). As there's currently no cure for the disease, a neurologist can prescribe steroids for specific symptoms. Other treatments to reduce the number of relapses might also be considered. Generally speaking, a neurologist can prescribe these treatment options after checking your mental status, speech, and reflexes (via WebMD). They may also order you to take other tests, including imaging tests, to look for damage in the brain, nerves, and blood vessels.