How Is Tuberculosis Treated?
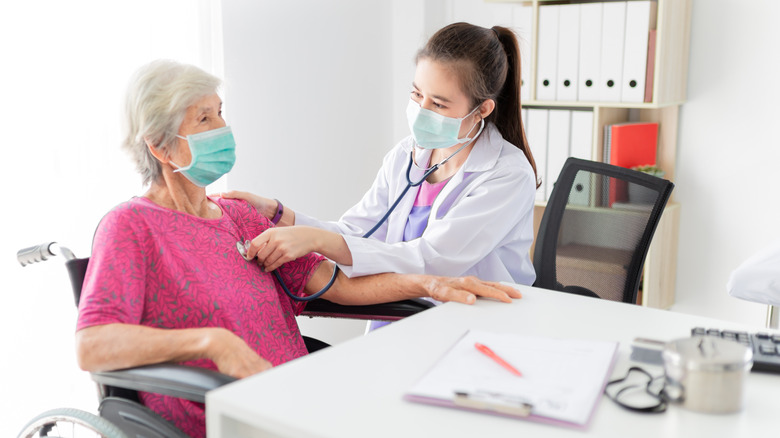
Tuberculosis is a serious and potentially deadly infection that primarily affects the lungs. It is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and it can be treated with antibiotics. However, if it is not treated properly, it can spread to other parts of the body and become very difficult to cure. Treatment for tuberculosis usually involves a combination of antibiotics. The most common drugs used to treat TB are called isoniazid, rifampin, and a combination of isoniazid and rifapentine. These drugs are usually taken for three to nine months (via WebMD). In some cases, they may be taken for up to two years. It is important that the full course of treatment is completed, even if the symptoms go away. If the treatment is stopped too soon, the infection can come back and be even more difficult to treat.
The first line of defense against tuberculosis is preventing it from spreading. If you have tuberculosis, it is important to stay away from other people as much as possible. Wear a mask when you are around others and avoid close contact, such as hugging or kissing. You should also wash your hands often, especially after coughing or sneezing. If you think you might have tuberculosis, it is important to see a doctor right away. Treatment for tuberculosis can usually be started right away if the infection is caught early.
What is tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a serious lung infection caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is spread through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Tuberculosis can also be spread through contact with infected blood, urine, or saliva (via Mayo Clinic). Anyone can get tuberculosis, but some people are more at risk than others. These include people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, and people who smoke. Tuberculosis is a leading cause of death worldwide, but it is curable with antibiotics (via The World Health Organization).
If you have tuberculosis, you may not have any symptoms at first. But over time, the infection can damage your lungs and make it hard to breathe. Other symptoms of tuberculosis include coughing up blood, fatigue, weight loss, and fever. If the infection is not treated, it can be fatal. If you think you might have tuberculosis, see your doctor right away. He or she will likely order a chest X-ray and a skin test or blood test to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment for tuberculosis usually involves taking antibiotics for several months. In some cases, you may also need to have surgery to remove the infected tissue from your lungs. With treatment, most people with tuberculosis can make a full recovery.