This Is How Long It Takes For Chemo To Start Working
Claiming 10 million lives in 2020 alone, cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, per the World Health Organization. Despite this bad news, the various treatment options for cancer seem promising. One such option is chemotherapy, which is an aggressive treatment used to destroy rapidly growing cancer cells (via Healthline).
According to the American Association for Cancer Research, chemotherapy was first introduced in the 20th century. In 2019, the American Journal of Managed Care estimated that the annual demand for chemotherapy will rise by 53% between 2018 and 2040, indicating the drug's effectiveness in treating cancer.
Most chemotherapy treatments are administered intravenously (via Mayo Clinic). However, oncologists can also administer chemotherapy using needles, pills, or creams.
If you're about to undergo treatment, you might wonder how long it takes for chemotherapy to start working. Continue reading as we detail the onset of action for chemotherapy and the various side effects associated with the treatment.
How long does it take for chemotherapy to start working?
According to Medical News Today, some forms of chemo act more quickly than others. The source notes that topical chemo medications can be rubbed directly onto cancerous cells whilst oral medications need to reach the bloodstream before they can work. However, it's important to note that most cancer treatments are done in cycles, ranging from two to six weeks, according to the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Your oncologists might base your chemo administration cycle on various factors, including the type and stage of your cancer, the goal of the treatment, and the type of chemo drugs used, per Healthline. Given this, changes in cycle plans can happen, which may affect how long the treatment takes to work.
Since everyone's body responds differently to chemotherapy, Healthline notes that it is difficult to provide a timeline of exactly when the treatment will start working. For some patients, it might start working immediately; for others, it will take months. According to Cancer Research UK, an entire course of chemotherapy typically lasts between three to six months.
Common side effects of chemotherapy
Although chemotherapy is a trusted treatment for several cancer types, it's been associated with scores of side effects; some are mild and treatable, while others lead to serious complications, according to Mayo Clinic. Chemo drugs travel throughout the body, killing fast-growing cancerous cells, while also affecting normal and healthy cells, leaving patients vulnerable to various health risks (via the American Cancer Society).
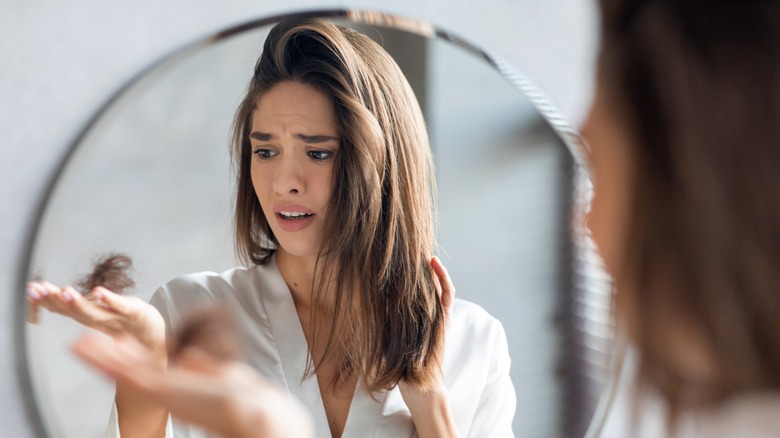
According to the National Health Service (NHS), fatigue, sore mouth, bleeding, and nausea are a few common side effects of chemo. Infections are also common. Chemotherapy can damage the immune system, reducing the number of white blood cells which fight infections, per Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A 2019 study published in the Indian Dermatology Journal Online highlights hair loss as another common side effect of chemotherapy, with an estimated incidence of 65%.
Consult with your doctor if you notice any concerning side effects.