Unexpected Reasons Your Ears Feel Clogged
A variety of health issues can lead to an individual experiencing a feeling of fullness within their ears. These include acoustic neuroma, allergies, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction, to name a few (via Healthline).
The Mayo Clinic defines an acoustic neuroma as a noncancerous, slow-growing tumor that develops on the vestibular nerve leading from your inner ear to your brain. This neuroma is caused by Schwann cells that grow and cover the vestibular nerve. The nerve sends information to the brain from the inner ear to help with balance and head positioning (via the Cleveland Clinic). Hearing loss associated with acoustic neuromas can lead to feelings of fullness within the ear, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine.
The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America states that in 2018, approximately 24 million people in the U.S. were diagnosed with seasonal rhinitis, impacting 8% of adults and 7% of children. Symptoms of seasonal rhinitis include congestion, postnasal drip, and eye irritation (via the Mayo Clinic). Postnasal drip and congestion cause mucus to block the eustachian tube, preventing drainage to the throat from the inner ear (via WebMD).
TMJ dysfunction occurs when the muscles and ligaments around your jaw become inflamed or irritated. The condition may be acute or chronic, resulting in mild or severe pain. Misalignment and mechanical issues can affect how your TMJ is moving, causing it to slip backward. This puts pressure on nerves and blocks the ear (via Atlas Healthcare).
What is the best way to treat clogged ears?
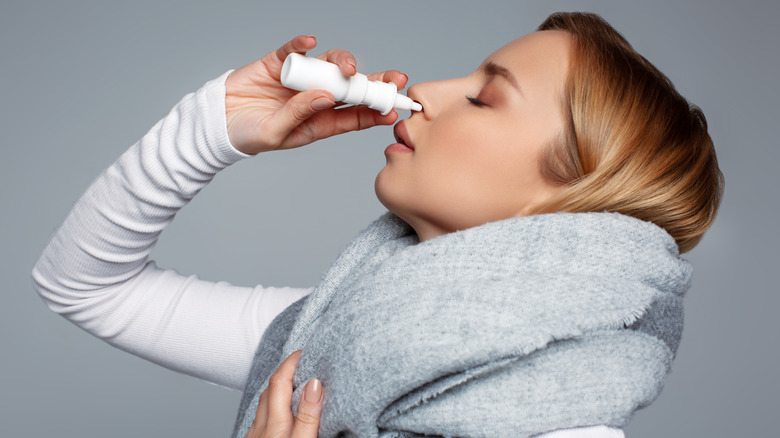
Allergies are a common cause of clogged eustachian tubes. Many individuals may require the use of antihistamines to combat their allergies and the inflammation leading to blocked eustachian tubes. Other medications that can help with clogged ears are nasal or oral decongestants, topical nasal steroids, and ear drops (via the Mayo Clinic).
Along with medical intervention, there are other options that can be used at home to ease the symptoms of clogged ears. Steam can expand the nasal passages, allowing the sinuses to drain. This can relieve the pressure of blocked eustachian tubes due to allergies or infection. Simply boil a pot of water and inhale its steam, or take a hot shower (via MedicalNewsToday). Another remedy that can be done at home is the Valsalva maneuver. This technique unclogs ears by forcing air through the sinuses and eustachian tubes, relieving pressure built up in the eustachian tube of the inner ear. To successfully perform this maneuver, close your mouth, pinch your nose shut, and press the air out like you are blowing up a balloon (via Mercy Health).
Other options for treating clogged ears at home include using a humidifier to avoid your sinus membranes drying out, spraying your nose with saline twice a day to maintain adequate moisture levels, and staying hydrated. You can also use over-the-counter pain relievers for pain and inflammation related to sinus pressure and eustachian tube blockage (via WebMD).
When should you see a healthcare professional to address clogged ears?
In cases where clogged ears don't resolve, it's imperative that you speak with a healthcare professional to address your hearing concerns. When clogged ears cannot be resolved at home with over-the-counter medications and other remedies, more invasive treatment options may be necessary to drain the blocked eustachian tube (via MedicineNet).
Surgery is often recommended for patients experiencing chronic ear blockage. One procedure that helps eustachian tube draining involves inserting a small ear tube within the eardrum. This tube allows excess fluid to drain out of the ear, and it is a low-risk procedure that can be done during a visit to your otolaryngologist (via the Mayo Clinic). According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, risks of ear tube placement include eardrum scarring, bleeding, hearing loss, infection, and chronic ear drainage. Other procedures that can alleviate symptoms of clogged eustachian tubes are the correction of a deviated septum or cleft palate. Your healthcare provider will order CT scans of your temporal bones to see if there are abnormalities within the bony structures of your ears or nose (via Cedars-Sinai).
After reviewing your results, your provider will discuss which treatment options are best for you. When discussing the options with your healthcare provider, be sure to identify the potential benefits, as well as the risks associated with the choices presented to you.